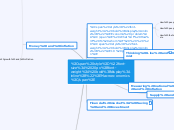
Macroeconomics
Economic problem: What? How? To whom? 10 principles
How people make decisions
How people interact
How the economy works as a whole
Thinking Like and Economist
Measuring national income and inflation
Supply and demand
Financial market: Saving and Investment
Money and inflation
The monetary system
the meaning of money
the role of central banks
European central banks and eurosystem
The bank of England
Money growth and inflation
Classical theory of inflation
The level of prices and the value of money
Level of Pries
value of money measured in G/S
price of basket
Value of Money
amount of G/S you can exchange for money
Money supply, demand and equilibrium
Money supply: Central banks
Money demand: how much wealth people want to hold in liquid form
The effects of monetary injection = [expansionary fiscal policy] Buy-in gov. Bonds from public in open market operations
Increase in Money supply
Decrease Value of Money
Increase in Price level
Adjustment period
Equilibriumm A
Increase in Money supply
Increase in Value of Money
Increase in Demand G/S
Increase in Price Level
Increase in Demand for money
Equilibrium B
Classical Dichotomy of Money neutrality
Changes in Money supply do not affect real values