Mesoamerica
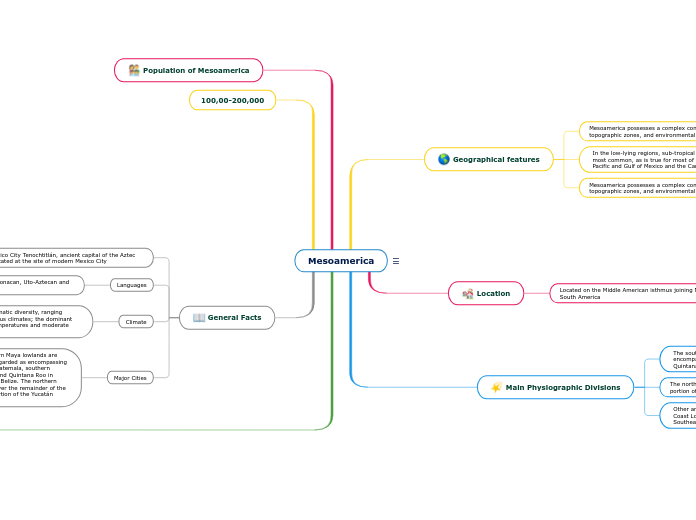
Geographical features
Mesoamerica possesses a complex combination of ecological systems, topographic zones, and environmental contexts.
In the low-lying regions, sub-tropical and tropical climates are most common, as is true for most of the coastline along the Pacific and Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
Mesoamerica possesses a complex combination of ecological systems, topographic zones, and environmental contexts.
Location
Located on the Middle American isthmus joining North and South America
Main Physiographic Divisions
The southern Maya lowlands are generally regarded as encompassing northern Guatemala, southern Campeche and Quintana Roo in Mexico, and Belize.
The northern lowlands cover the remainder of the northern portion of the Yucatán Peninsula
Other areas include Central Mexico, West Mexico, the Gulf Coast Lowlands, Oaxaca, the Southern Pacific Lowlands, and Southeast Mesoamerica
Population of Mesoamerica
100,00-200,000
General Facts
Mexico Mexico City Tenochtitlán, ancient capital of the Aztec empire. Located at the site of modern Mexico City
Languages
ayan, Oto-Mangue, Mixe–Zoque, Totonacan, Uto-Aztecan and Chibchan languages
Climate
The highlands show much more climatic diversity, ranging from dry tropical to cold mountainous climates; the dominant climate is temperate with warm temperatures and moderate rainfall
Major Cities
The southern Maya lowlands are generally regarded as encompassing northern Guatemala, southern Campeche and Quintana Roo in Mexico, and Belize. The northern lowlands cover the remainder of the northern portion of the Yucatán Peninsula.