Newtons 3 laws of motion
Newtons First Law of Motion
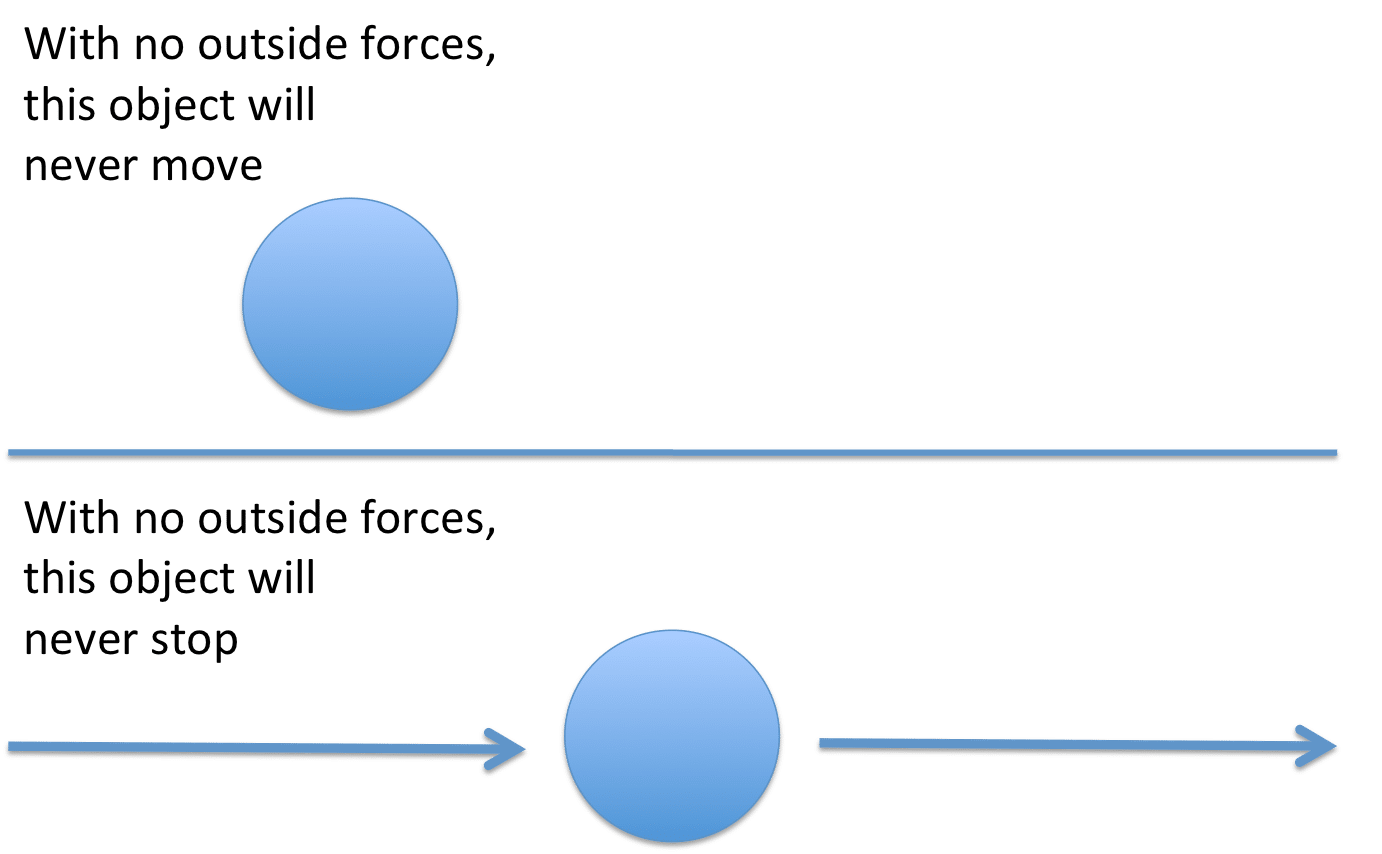
An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Ex: A golf ball sitting on a tee.
Ex: A person sitting in a chair.
Newton's Second Law of Motion

Acceleration is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object).
Mike's car, which weighs 1,000 kg, is out of gas. Mike is trying to push the car to a gas station, and he makes the car go 0.05 m/s/s. Using Newton's Second Law, you can compute how much force Mike is applying to the car by doing mass times acceleration = force.
Ex: An object moving with 2m/s times m/s and 3 kg of mass will have 6N of force.
Newton's Third Law of Motion
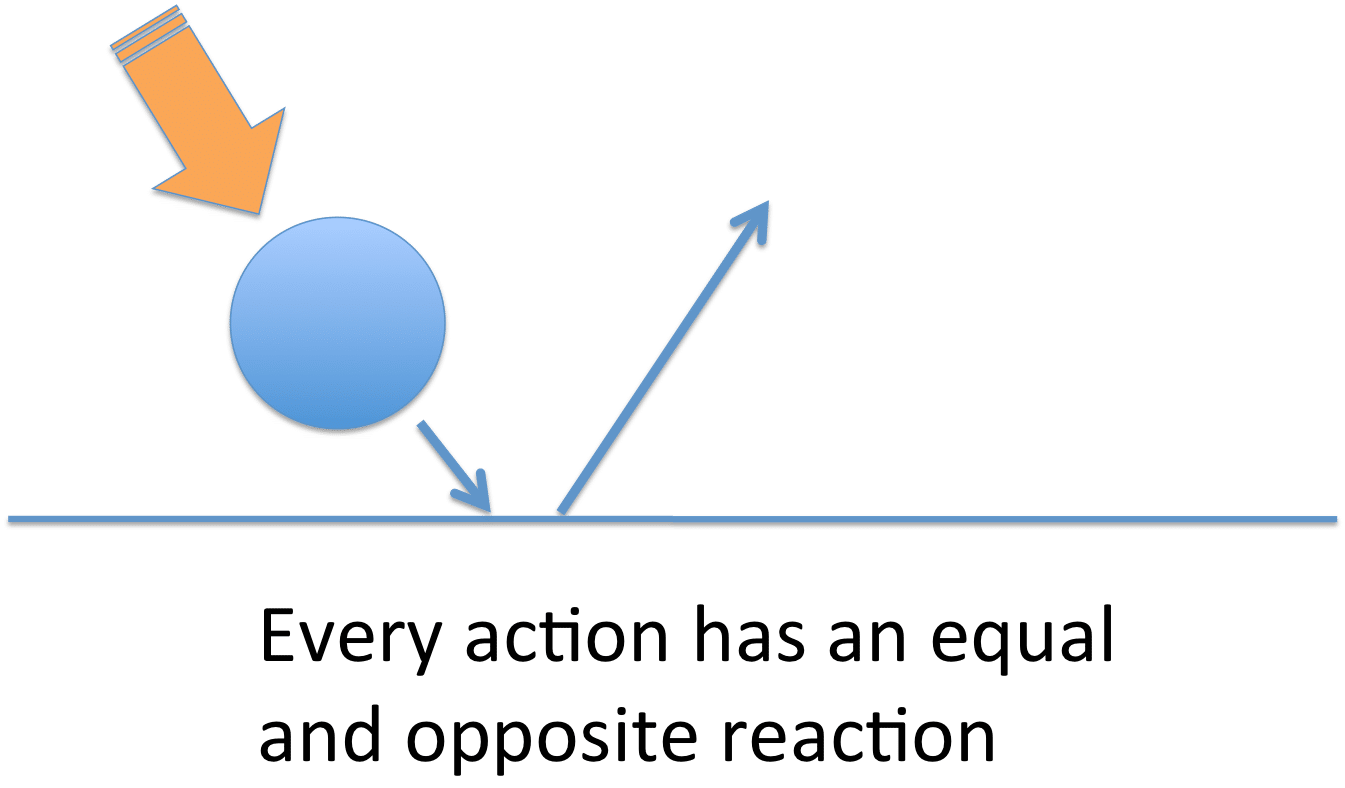
For every action there is an equal and opposite re-action.
Ex: When a cue ball hits a billiard ball the billiard ball will move forward.
Ex: Newtons cradle works when one ball hits the others the ball on the end will move also.