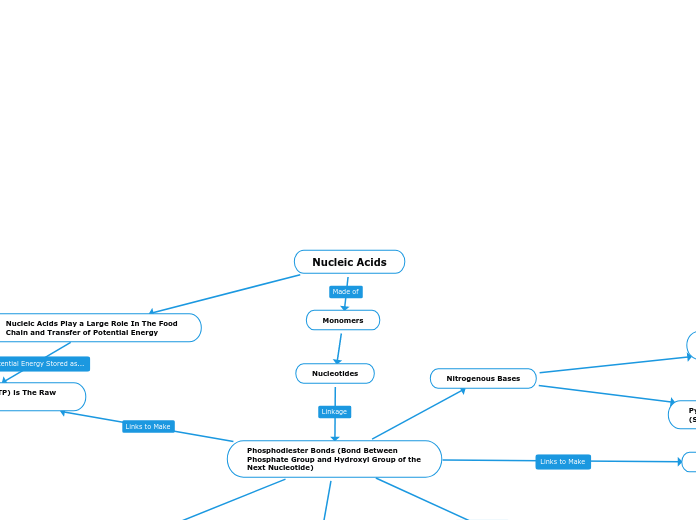
Nucleic Acids
Monomers
Nucleotides
Phosphodiester Bonds (Bond Between Phosphate Group and Hydroxyl Group of the Next Nucleotide)
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is The Raw Form Of Energy
3 Phosphate Groups + Ribose Sugar + Adenine
Autotrophs (Organisms That Produce Their Own Energy Like Plants). Make Their Own ATP Using Sunlight
Heterotrophs (Organisms That Need To Consume Their Energy Like Humans) Consume Their Energy, But Can Only get 5-20% of The Original Energy
Dinucleotides
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
Two Phosphate Groups + Two Ribose Sugar + Adenine + Nicotinamide
Nicotinamide Adenine
Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADP+)
Two Phosphate Groups + Two Ribose Sugar + Adenine + NADH Group
Used In Different Sets of Reactions That Remove Hydrogen (Ex. Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis)
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
Two Phosphate Groups + Two Ribose Sugars + Adenine + Riboflavin)
Coenzyme A (CoA)
Two Phosphate Groups + Ribose + Adenine + Phosphoadenosine Diphosphate + Pantothenic Acid + Beta Mercaptoethylamine
Used to Move a Molecule to An Enzyme
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP)
Phosphate Group + Ribose + Adenine + Hydroxyl
A Second Messenger for Internal Signalling In The Cells
Nitrogenous Bases
Purines = Adenine, Guanine (Double Ring Structure)
Pyrimidines + Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil (Single Ring Structure)
Nucleic Acids Play a Large Role In The Food Chain and Transfer of Potential Energy
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Phosphate + Ribose Backbone and Nitrogenous Base (Single Stranded)
Adenine Bonds with Uracil
(Two Hydrogen Bonds. Uracil Replaces Thymine in RNA), Guanine Bonds with Cytosine (Three Hydrogen Bonds)
Functions
Participates In Protein Synthesis
Transcribes and Translates DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Phosphate + Deoxyribose Backbone and Nitrogenous Base (Double Stranded Helix)
Adenine Bonds with Thymine (Two Hydrogen Bonds), Guanine Bonds with Cytosine (Three Hydrogen Bonds)
Long Term Storage of Genetic Information