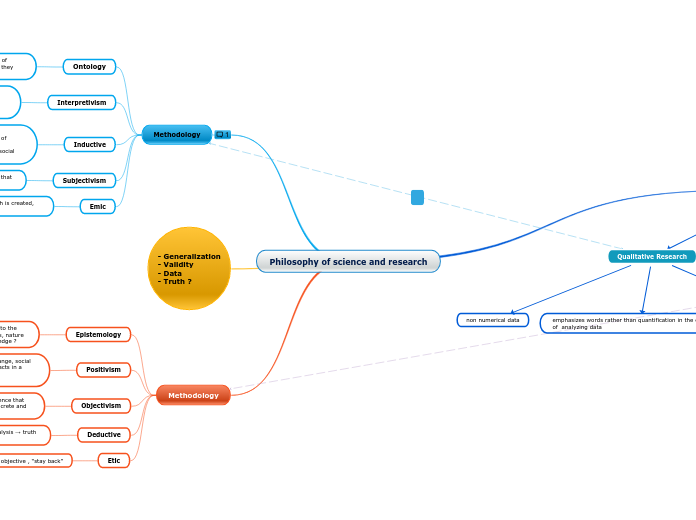
Philosophy of science and research
Research Methods
Qualitative Research
non numerical data
emphasizes words rather than quantification in the collection of analyzing data
"context means everything"
Quantitative Research
systematic empirical investigation
collecting and analyzing numerical data
Methodology
Ontology
beliefs about reality, our perception of truth, the nature of reality, what entities operate within the reality and how they interrelate to each other
Interpretivism
“ feeling” researches , how do humans make sense of the world around them? , multiple realities shaped by context, understanding interpretations, experience of individuals/groups ,empathy with their subjects
Inductive
pattern analysis → hypothesis → theory
development of a theory as a result of the observations of empirical data
goal of understanding a particular phenomena within a social context
Subjectivism
social phenomena is created from the perception that
social life is the product of social interactions
Emic
subjective approach , interaction is needed, truth is created, “dig deep, get inside”
- Generalization
- Validity
- Data
- Truth ?
Methodology
Epistemology
theory of knowledge, social world is studied according to the same principles and procedures as the natural sciences, nature of knowledge, what is considered as acceptable knowledge ?
Positivism
generalizable, objective, one truth that does not change, social facts apart from the beliefs of an individual, social facts in a scientific and systematic way, structural forces, macroperspective, researchers are independent
Objectivism
social phenomena and their meanings have an existence that is independent of social actors, social world is as concrete and real as the natural world
Deductive
theory → hypothesis → pattern analysis → truth
starting with a theory
Etic
realism, truth can be measured, objective , “stay back”