PRICING STRATEGIES
Price
The sum of all the values that consumers give up in order to gain the benefits of having or using a product or service
Illegal actions
Pricing policy
Price Fixing
Predatory Pricing
Price Discrimination
Price Maintenance
Deceptive pricing
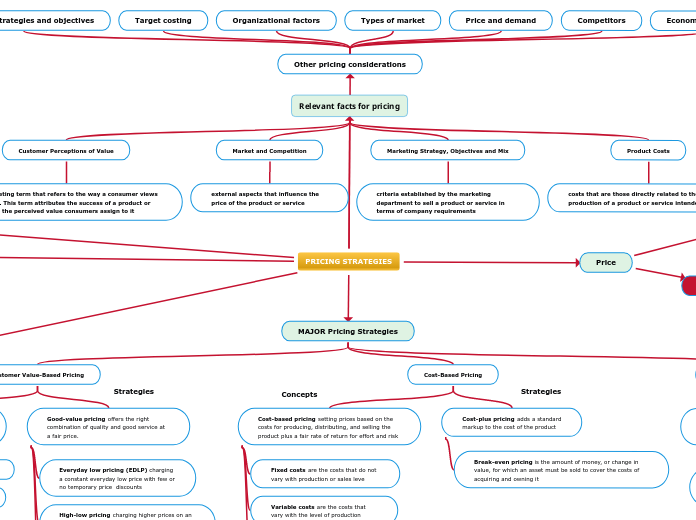
Relevant facts for pricing
Customer Perceptions of Value
is a marketing term that refers to the way a consumer views a product. This term attributes the success of a product or service to the perceived value consumers assign to it
Market and Competition
external aspects that influence the price of the product or service
Marketing Strategy, Objectives and Mix
criteria established by the marketing department to sell a product or service in terms of company requirements
Product Costs
costs that are those directly related to the production of a product or service intended for sale
MAJOR Pricing Strategies
Customer Value-Based Pricing
uses the buyersʼ perceptions of value, not the sellers cost, as the key to pricing
Value-based pricing: is customer driven
Cost-based pricing: is product driven
Price is considered before the
marketing program is set
Good-value pricing offers the right combination of quality and good service at a fair price.
Everyday low pricing (EDLP) charging a constant everyday low price with few or no temporary price discounts
High-low pricing charging higher prices on an everyday basis but running frequent promotions to lower prices temporarily on selected items
Value-added pricing attaches valueadded features and services to differentiate offers, support higher prices, and build pricing power
Cost-Based Pricing
Cost-based pricing setting prices based on the costs for producing, distributing, and selling the product plus a fair rate of return for effort and risk
Fixed costs are the costs that do not vary with production or sales leve
Variable costs are the costs that vary with the level of production
Total costs are the sum of the fixed and variable costs for any given level of production
Cost-plus pricing adds a standard
markup to the cost of the product
Break-even pricing is the amount of money, or change in value, for which an asset must be sold to cover the costs of acquiring and owning it
Competition-Based Pricing
Setting prices based on competitorsʼ strategies, costs, prices, and market offerings
Consumers will base their judgments
of a productʼs value on the prices that
competitors charge for similar products
Skim and Penetrate
Product mix
Product line
Optional product
Captive product
By-product
Product bundle
Price adjustment
Discount and
allowance
Segmented
Psychological
Promotional
Geographic
Dynamic
International
Other pricing considerations
Marketing strategies and objectives
Target costing
Organizational factors
Types of market
Price and demand
Competitors
Economic conditions