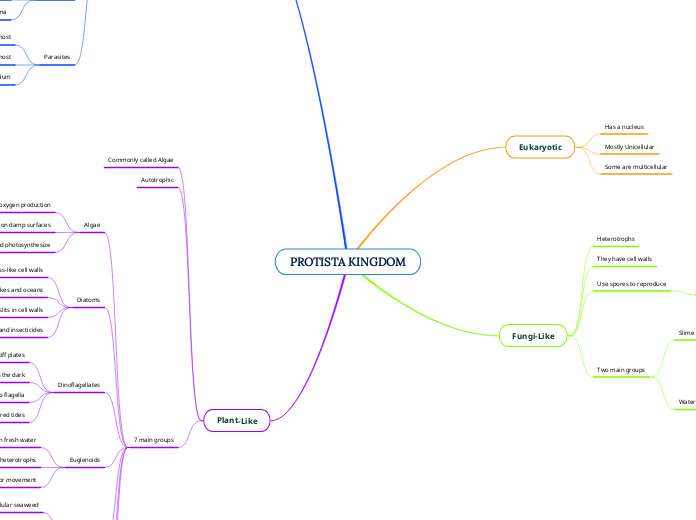
PROTISTA KINGDOM
Eukaryotic
Has a nucleus
Mostly Unicellular
Some are multicellular
Fungi-Like
Heterotrophs
They have cell walls
Use spores to reproduce
Spores are tiny cells that can grow
into a new organism
Two main groups
Slime Mold
Brightly colored
Lives in moist, shady places
They range from very tiny to as large as several meters
Water Molds and Downy Mildew
Most live in water
They grow in tiny threads
that look like fuzz
Responsible for Irish Potato Famine
Animal-Like
Called Protozoans
Heterotrophic
Can move
Does not have a cell wall
4 main groups:
Sarcodines
feed using pseudopods, or false feet
have a contractile vacuole, a structure that
collects and repels extra water
Example: amoeba
Ciliates
Use cilia to move and eat
*cilia are hair-like projections that move like oars in a wave-like motion
* cilia sweep food to the ciliates
Example: Paramecium
Flagellates
Use flagella, or a whip-like tail structure to move
Can have one or more flagella
Example: Paranema
Parasites
Feed on the cells and bodily fluids of their host
many have more than one host
Example: plasmodium
Plant-Like
Commonly called Algae
Autotrophic
7 main groups
Algae
Very important in oxygen production
Most live in water, some live on damp surfaces
All algae contain chlorophyll and photosynthesize
Diatoms
Have glass-like cell walls
Float near surface of lakes and oceans
move by oozing chemicals out of slits in cell walls
Used in scouring products and insecticides
Dinoflagellates
Surrounded by stiff plates
Come in a variety of colors, including glow in the dark
All have two flagella
Responsible for red tides
Euglenoids
Green, usually found in fresh water
autotrophs or heterotrophs
use flagella for movement
Red Algae
Multi-cellular seaweed
needs only small amount of sunlight
used in hair conditioner and ice cream
contains red chlorophyll
Green Algae
Contain green pigments
unicellular, multicellular, or colonial
Closely related to plants
Brown Algae
Seaweed with many pigments
Has many plant-like structures