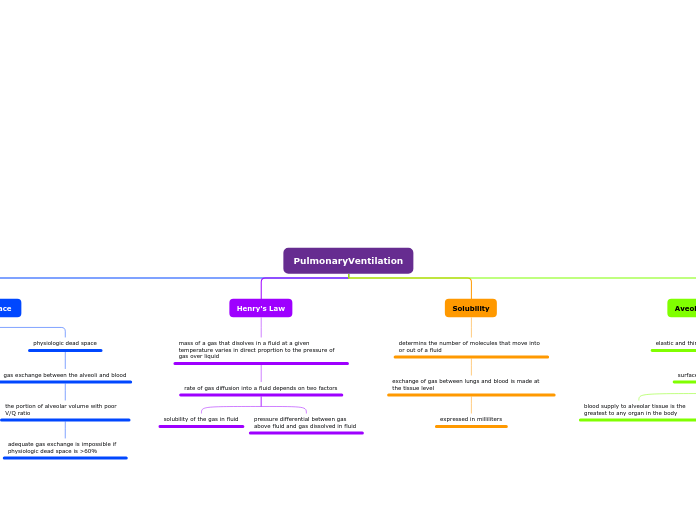
PulmonaryVentilation
dead space
anatomic dead space
not involved in gas exchange
volume or air that is in conducting airways
physiologic dead space
gas exchange between the alveoli and blood
the portion of alveolar volume with poor V/Q ratio
adequate gas exchange is impossible if physiologic dead space is >60%
Henry's Law
mass of a gas that disolves in a fluid at a given temperature varies in direct proprtion to the pressure of gas over liquid
rate of gas diffusion into a fluid depends on two factors
solubility of the gas in fluid
pressure differential between gas above fluid and gas dissolved in fluid
Solubility
determins the number of molecules that move into or out of a fluid
exchange of gas between lungs and blood is made at the tissue level
expressed in milliliters
Aveolar Ventilation
elastic and thin walled membranous sacs
surface for gas exchange
blood supply to alveolar tissue is the greatest to any organ in the body
at rest, 250 ml of O2 leave alveoli to blood, and 200 ml of CO2 diffuse into alveoli
during heavy exercise, 25X increase in quantity of oxygen transfer