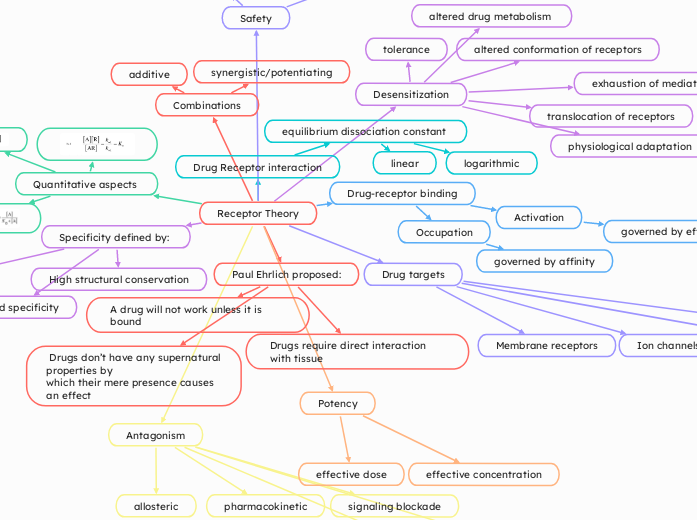
Receptor Theory
Paul Ehrlich proposed:
Drugs require direct interaction with tissue
A drug will not work unless it is bound
Drugs don’t have any supernatural properties by
which their mere presence causes an effect
Specificity defined by:
High structural conservation
ligand specificity
site specificity
Drug targets
Membrane receptors
Ion channels
carriers/transport molecules
enzymes
Drug-receptor binding
Occupation
governed by affinity
Activation
governed by efficacy
Drug Receptor interaction
equilibrium dissociation constant
linear
logarithmic
Quantitative aspects
Potency
effective dose
effective concentration
Antagonism
allosteric
pharmacokinetic
signaling blockade
physiological
chemical
Combinations
additive
synergistic/potentiating
Desensitization
tolerance
altered conformation of receptors
translocation of receptors
exhaustion of mediators
altered drug metabolism
physiological adaptation
Safety
Therapeutic Index
Certain safety factor