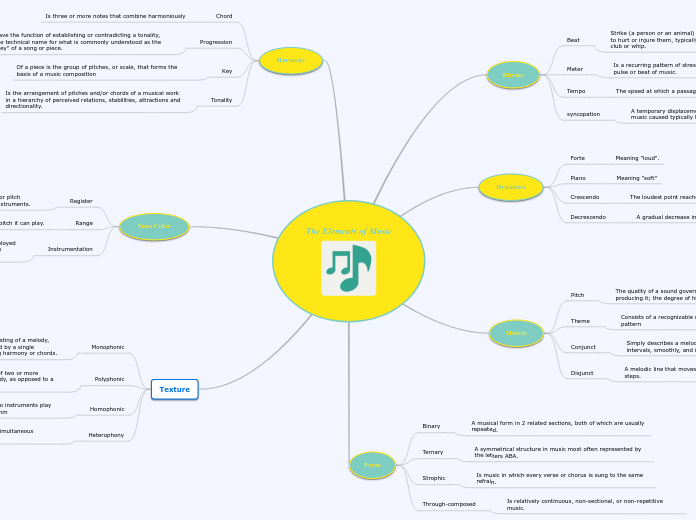
The Elements of Music

Rhyme
Beat
Strike (a person or an animal) repeatedly and violently so as to hurt or injure them, typically with an implement such as a club or whip.
Meter
Is a recurring pattern of stresses or accents that provide the pulse or beat of music.
Tempo
The speed at which a passage of music is or should be played.
syncopation
A temporary displacement of the regular metrical accent in music caused typically by stressing the weak beat
Dynamics
Forte
Meaning "loud".
Piano
Meaning "soft"
Crescendo
The loudest point reached in a gradually increasing sound.
Decrescendo
A gradual decrease in volume of a musical passage.
Melody
Pitch
The quality of a sound governed by the rate of vibrations producing it; the degree of highness or lowness of a tone.
Theme
Consists of a recognizable melody or a characteristic rhythmic pattern
Conjunct
Simply describes a melody that moves in distinct steps or intervals, smoothly, and in a connected way.
Disjunct
A melodic line that moves by leaps and skips rather than in steps.
Form
Binary
A musical form in 2 related sections, both of which are usually repeated.
Ternary
A symmetrical structure in music most often represented by the letters ABA.
Strophic
Is music in which every verse or chorus is sung to the same refrain.
Through-composed
Is relatively continuous, non-sectional, or non-repetitive music.
Harmony
Chord
Is three or more notes that combine harmoniously
Progression
Have the function of establishing or contradicting a tonality, the technical name for what is commonly understood as the "key" of a song or piece.
Key
Of a piece is the group of pitches, or scale, that forms the basis of a music composition
Tonality
Is the arrangement of pitches and/or chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, attractions and directionality.
Tone Color
Register
Is the "height" or range of a note, set of pitches or pitch classes, melody , part, instrument, or group of instruments.
Range
Is the distance from the lowest to the highest pitch it can play.
Instrumentation
Is the particular combination of musical instruments employed in a composition, and the properties of those instruments individually
Texture
Monophonic
Is the simplest of musical textures, consisting of a melody, typically sung by a single singer or played by a single instrument player without accompanying harmony or chords.
Polyphonic
Is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice>
Homophonic
Is a piece of music with chords, where two instruments play the same line of melody in the same rhythm
Heterophony
Is a type of texture characterized by the simultaneous variation of a single melodic line