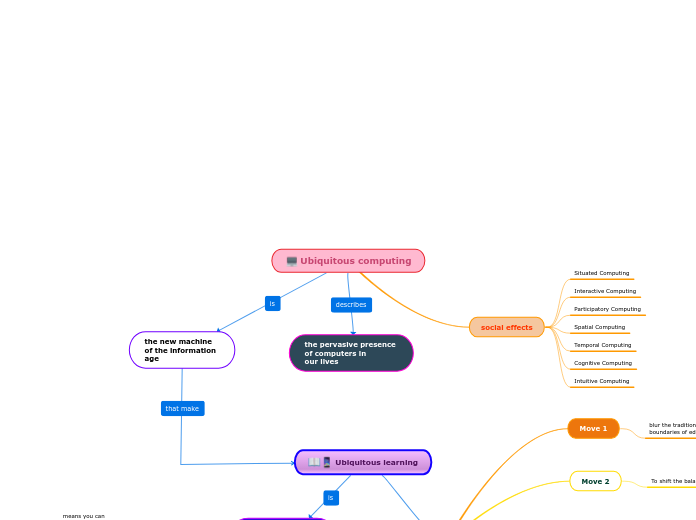
Ubiquitous computing
social effects
Situated Computing
Interactive Computing
Participatory Computing
Spatial Computing
Temporal Computing
Cognitive Computing
Intuitive Computing
Ubiquitous learning
the new machine of the information age
a new educational paradigm made possible in part by the affordances of
digital media.
affordance
means you can
do some things easily now, and you are more inclined to do these things than you were before simply
because they are easier
the pervasive presence of computers in
our lives
Seven moves which are characteristic of ubiquitous learning
Move 1
blur the traditional institutional, spatial and temporal boundaries of education
Move 2
To shift the balance of agency
Move 3
Recognise learner differences and use them as a productive resource
Move 4
Broaden the range and mix of representational modes
Move 5
Develop conceptualising capacities
Move 6
Connect one’s own thinking into the social mind of distributed cognition
Move 7
Build collaborative knowledge cultures