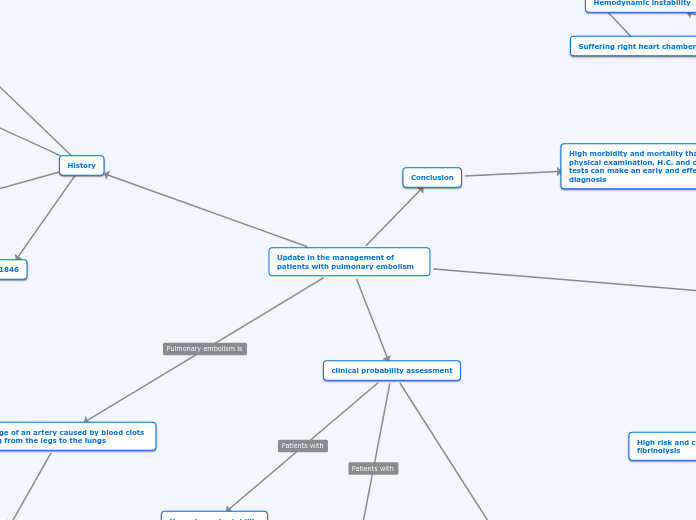
Update in the management of patients with pulmonary embolism
Blockage of an artery caused by blood clots moving from the legs to the lungs
Clinical presentation
variability from
dyspnoea
Tachypnea
Haemoptysis
Syncope
Shock
History
clinical probability assessment
Hemodynamic stability
Dimero D
Multislice tomography
hemodynamically stable
Tomography
Criteria to use
Wells
Probable
De 0 a 4
Unlikely
Greater than 4
Evaluate
Predisposing factors
Clinical probability
Signs and symptoms
clinical judgment
Ginebra
Evaluate
Predisposing factors
Clinical probability
Signs and symptoms
High
Greater than 10
Intermediate
4-10
Low
0-3
Take Dimero D's lab
Biological marker product of fibrin degradation
8 Hours
It is not reliable for the diagnosis of embolism, it is part of the diagnosis of
Trauma
Nephropathies
Sepsis
Peripheral arthropathies
Treatment
Pulmonary embolism
It is managed outpatient when
hemodynamic stability
Low risk
Treated with
External consultation
HBPM
Mass pulmonary embolism
Anticoagulation
Alteplasa 100 mg in the first 2 hours
Scheme that decays due to the change to the accelerated administration mode
1,5 millions of units in 2 hours
Anticoagulation
Streptokinasa 250.000 UI in
the first 30 minuts
100.000 UI every hour for 24 hours
Surgical pulmonary embolectomy
High risk and contraindication for fibrinolysis
After the procedure is performed
Normotechnical cardiopulmonary bypass
persistent hemodynamic instability
Pregnant patients
Greenfield filter infrarenal position
Diagnostic means
TAC scan of the chest on pulmonary angiography
Hemodynamic instability
HBPM
Suffering right heart chambers
Conclusion
High morbidity and mortality than with physical examination, H.C. and diagnostic tests can make an early and effective diagnosis
1761
1576
1846
600-100 B.C.
ayurveda medicine
French surgeon
A process of blood clotting function without identifying the mechanism
Giovanm Basttista
The presence of clots in the veins of patients suffering from sudden death
Endothelial damage
Rudolph Virchow
Describes a triad
Stasis
Hypercoagulability
Clots are carried through the bloodstream
transesophageal echocardiogram
60%
90%
Paradoxical movement of the interventricular septum
systolic dysfunction of the right ventricle
Pulmonary hypertension
venous filter
Patients contraindicated for anticoagulation
Patients with high risk of pathology recurrence
Floating emboli in the inferior vena cava