NUR BALQIS BINTI MUSTAZIM 190154
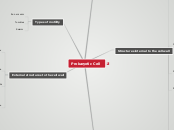
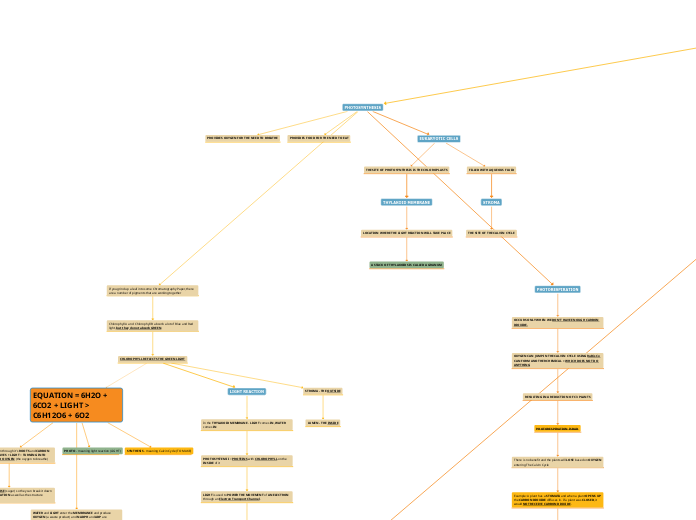
Prokaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic CellCharacteristicsSmaller in sizeNo membrane bound organellesCell division by binary fissionTypes of motilityRun or swimTumblesSwarmStructures internal to the cell wallPlasma membraneMechanical boundary of cell, nutrientand waste transportLocation for metabolic processesDetection of environmental cuesfor chemotaxisCytoplasmsubstance of the cell within plasma membraneconsist of 80% water and primarily contain protein, carbohydrates and lipidsNuclear area or nucleoidcontain genetic informationRibosomessites for protein synthesisInclusionsStorage of carbon, phosphate and other substanceExternal structures to the cell wallGlycocalyxAttachment to surfaceProtect against dehydrationInhibit movement of nutrients out of cellsSource of nutrientsFlagellaLong filamentous appendages for motilityAxial filamentsPresent in spirochetesKnown as endoflagellaFor corkscrew movementFimbriaeOccur at poles or distributed over the entire surfaceFunction as attachmentCell WallResponsible for the shape of cellPrevent bacterial cells from rupturing due to changes in pressureThe point of anchorage for flagellaMay contain antigen if bacteria is infectiousTypes of cell wallGram +veGram -veAtypica
External structures to the cell wall
Fimbriae
Function as attachment
Occur at poles or distributed
over the entire surface
Axial filaments
For corkscrew movement
Known as endoflagella
Present in spirochetes
Flagella
Long filamentous appendages for motility
Glycocalyx
Source of nutrients
Inhibit movement of nutrients out of cells
Protect against dehydration
Attachment to surface
Types of motility
Swarm
Tumbles
Run or swim
Cell wall
Types of cell wall
Gram -ve
Gram +ve
May contain antigen if the bacteria is infectious
The point of anchorage flagella
Prevent bacterial cells from rupturing due to the change in pressure
Responsible for the shape of the cell
Structures internal to the cell wall
Endospore
Inclusions
Types of inclusions
Gas vesicles
Magnetosomes
Iron oxide (Fe3O4) that act like magnet
Carboxysomes
Used for co2 fixation during photosynthesis
Contain the enzyme ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase
Sulfur granules
Thiobacillus - sulfur bact.
Derive energy
sulfur-containing compounds
oxidising sulfur
Energy reserve
Lipid inclusios
Storage material -polymer poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid
Polysaccharide granules
Diffentiate by using iodine
starch granules: blue
glycogen granules: reddish brown
Consists glycogen and starch
Metachromatic granules
Stain red with certain blue dyes such as methylene blue
Large inclusions
Storage of carbon, phosphate and
other substance
Ribosomes
RNA or rRNA
sites for protein synthesis
Nuclear area or nucleoid
Plasmid
contain genetic information
Cytoplasm
Intracytoplasmic membranes
Anammoxosome in Planctomycetes
Plasma membrane infoldings
consist of 80% water and
primarily contain protein,
carbohydrates and lipids
substance of the cell within plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
The movement of materials across membranes
Active process
Group translocation
Active transport
Passive processes
Osmosis
Facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion
Uptake of Nutrients - Getting Through Barriers
Some unique substances may required
Micronutrients (trace elements)
Macroelements (macronutrients)
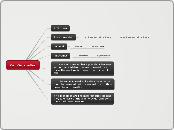
Destruction
Disinfectants - alcohols and quatenary ammonium compounds
Lysis: cells burst
Plasmolysis: cells shrink
Cause leakage of intracellular contents
Function
Captures energy as ATP
Carries on respiration
Assists in DNA replications
Synthesis cell wall components
Selectively permeable barrier
Detection of environmental cues
for chemotaxis
Location for metabolic processes
Mechanical boundary of cell, nutrient
and waste transport
Characteristics
Cell division by binary fission
No membrane bound organelles
Smaller in size