TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME
Type in the name of your subject.
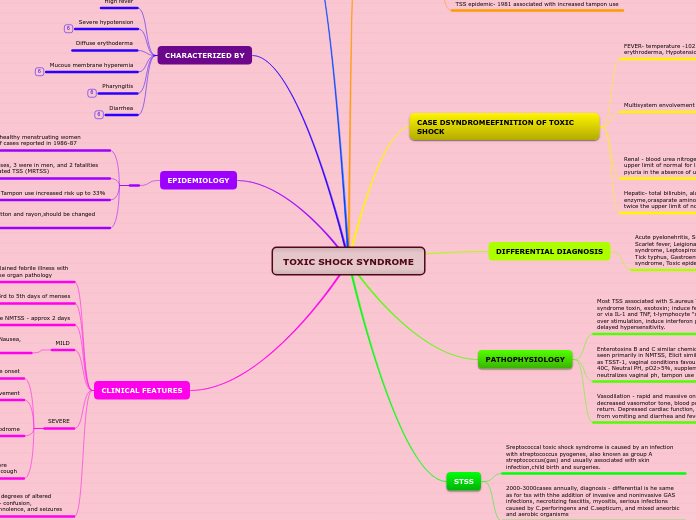
CLINICAL FEATURES
Add detailed notes about each lecture, so that when the time comes to prepare for exams, you will have an easier and quicker overview.
Focal neuro findings are rare, Varying degrees of altered consciousness, Toxic encephalopathy - confusion, disorientation, agitation, hysteria, somnolence, and seizures
SEVERE
orthostatic lightheadedness, profuse watery diarrhea, sore throat, paresthesias, photophobia, abdominal pain, and cough
Prodrome
Sudden onset of fevers and chills 1-4days prior to presentation
Headache, malaise, myalgia, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea
Early multiorgan envolvement
Acute onset
MILD
Fever, Chills, Myalgias, Abdominal pain, Sore throat, Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Self-limitng
Postoperative NMTSS - approx 2 days
Pts with NMTSS present 3rd to 5th days of menses
Homework
Add a short description of your homework and any details you need in order to understand and complete the task.
Check your knowledge
Add a list of questions to help you recap your lecture.
Discussion
Write down if there are things you would like to discuss or clarify with your teacher or colleagues in relation to this topic.
Introduction
Add a short description of the lecture.
TSS must be considered when- unexplained febrile illness with erythroderma, hypotension, and diffuse organ pathology
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Add here all the details about your projects.
CHARACTERIZED BY
Schedule your course ahead. Knowing all the information will make everything easier.
Diarrhea
Pharyngitis
Mucous membrane hyperemia
Diffuse erythoderma
Severe hypotension
Class name
Add class name.
Day, Date,Hour
Add additional information about this class.
High fever
Add the class information for each week.
TREATMENT
Add key information about the books you've read. If you feel it's necessary, you can add a small summary of your readings in the Notes section.
Aggressive shock management, Continuous monitoring: central Aggressive fluid replacement- 4-20L crystalloid and FFP, Ventilatory management if ARDS develpos complete blood work and cultures, removal of foreign bodies,i.e tampon or nasal packing, Antistaphlococcal penicilin or cephalospori. Pt not treated with beta-lactamase-stable abx can have recurrence, MRTSS - recurrence occcur in second month aftetr the innitial disease, recurring on the same day of the menstrual cycle, Initisl episode is the most severe.
Book title
Add summary of the content of a book
Availability
Add details about where you can get it from. For e.g.: library, bookstore, audiobook, etc.
Publishing information
Add the publishing information.
Author
Name the author.
STSS
2000-3000cases annually, diagnosis - differential is he same as for tss with thhe addition of invasive and noninvasive GAS infections, necrotizing fasciitis, myositis, serious infections caused by C.perforingens and C.septicum, and mixed aneorbic and aerobic organisms
Sreptococcal toxic shock syndrome is caused by an infection with streptococcus pyogenes, also known as group A streptococcus(gas) and usually associated with skin infection,child birth and surgeries.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Vasodilation - rapid and massive onset, hypotension, decreased vasomotor tone, blood pooling, decreased vascular return. Depressed cardiac function, total body water deficits from vomiting and diarrhea and fever.
Enterotoxins B and C similar chemical structure to TSST-1 seen primarily in NMTSS, Elicit similar clinical manifestations as TSST-1, vaginal conditions favourable to TSST-1, temp 39-40C, Neutral PH, pO2>5%, supplemental CO2, menstruation - neutralizes vaginal ph, tampon use may increase O2 and CO2.
Most TSS associated with S.aureus TSST-1; toxic shock syndrome toxin, exotoxin; induce fever via the hypothalamus or via IL-1 and TNF, t-lymphocyte "superantigenation" and over stimulation, induce interferon productiion, enhance delayed hypersensitivity.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Review your resource requirements and tick off the devices you will need as well as their availability. Add others, if necessary.
Acute pyelonehritis, Septic shock, Acute rheumatic fever, Scarlet fever, Leigionare's disease, PID, HUS, Acute viral syndrome, Leptospirosis, SLE, Rocky mountain spotted fever, Tick typhus, Gastroenteritis, Kawasaki disease, Reye syndrome, Toxic epidermic necrolysis, Erythema multiforme
Add other resources:
CASE DSYNDROMEEFINITION OF TOXIC SHOCK
Hepatic- total bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase enzyme,orasparate aminotransferase enzyme levels at least twice the upper limit of normal for laboratory.
Renal - blood urea nitrogen or ceatinine at least twice the upper limit of normal for laboratory or urinary sediment with pyuria in the absence of urinary tract infection
Multisystem envolvement
Mucous membrane - vaginal, oropharyngeal, or conjunctival hypermia
Muscular -serve myalgia or creatine phosphokinaselevel at least twice the upper limit of normal
GI- vomiting or diarrhea at onset of illness
FEVER- temperature -102.0F , rash-diffuse macular erythroderma, Hypotension
INTRODUCTION
Type in all the info you would like to know about this subject. If there is something you don't know yet, no problem! You can fill in the blanks along the way.
TSS epidemic- 1981 associated with increased tampon use
Type in the name of your teachers and teacher assistants, plus any details you should know about them.
Discovered in 1978 in apparently healthy children- staph aureus isolated
Add details about your course.
MUSCULAR -sever myalgia or creatine phosphokinase level at least twice the upper limit of normal