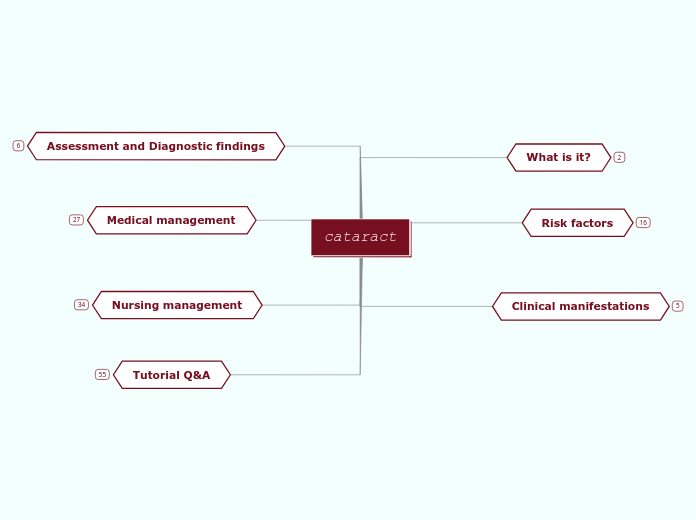
cataract
Tutorial Q&A
Q11: After cataract surgery, the nurse is right when she instructs the patient to avoid:
D. Using eyeglasses when going outside
C. Taking anticoagulants
B. Chewing on the same side of the operated area
A. Getting up from bed for 2 weeks after surgery
Q10: On ophthalmic examination, the nurse noted the major objective finding seen with cataracts:
C. Opaque lens
A. Tunnel vision
Q9: Upon assessment, the patient told the nurse that she was experiencing the three common symptoms found with cataracts and these are listed below except for:
D. Eye pain
C. Halos
B. Glare
A. Blurred vision
Q8: After cataract surgery, the patient is encouraged to:
D. Lift weights to increase muscle strength
C. Avoid bending his or her head below the waist
B. Lie on his or her stomach while sleeping
A. Maintain bed rest for one week
Q7: Nurse Kaye is carrying out her operative teachings for an older client who will have cataract surgery on the right eye. The nurse concludes that the client needs further understanding about the teachings if he says:
D. "I will bend below my waist frequently to increase circulation after surgery."
C. "I will call my physician if I have sharp and sudden pain or a fever after surgery."
B. "I will wipe my nose gently if it is congested after surgery."
A. "I will sleep on my left side after surgery."
Q6: The client is being discharged from the ambulatory care unit following cataract removal. The nurse provides instructions regarding home care. Which of the following, if stated by the client, indicates an understanding of the instructions?
D. “I will not lift anything if it weighs more that 10 pounds.”
C. “I will wear my eye shield at night and my glasses during the day.”
B. “I will sleep on the side that I was operated on.”
A. “I will take Aspirin if I have any discomfort.”
Q5: During the early postoperative period, the client who had a cataract extraction complains of nausea and severe eye pain over the operative site. The initial nursing action is to:
D. Turn the client on his or her operative side
C. Reassure the client that this is normal
B. Administer the ordered main medication and antiemetic
A. Call the physician
Q4: The nurse is developing a plan of care for the client scheduled for cataract surgery. The nurse documents which more appropriate nursing diagnosis in the plan of care?
D. Anxiety
C. Disturbed sensory perception
B. Imbalanced nutrition
A. Self-care deficit
Q3: Which one of the following advices would you give to the patient after Extra Capsular Cataract Extraction with Intra Ocular Lens Implant?
D. Avoid using the eye shield at night
C. Use warm compress every 8 hours
B. Avoid lifting heavy objects and prolonged bending
A. Lie down on the operated eye
Q2: The most common characteristic of Cataract is which one of the following symptoms?
D. Eye redness
C. Blurry vision
B. Diplopia (double vision)
A. Eye pain
Q1: Which one of the following is the most common contributing factor for developing Cataract and Glaucoma?
D. Sun Light
C. Trauma
B. Aging
A. Diabetes Mellitus
Nursing management
post-operative care
follow-up
educate patients about the importance of keeping their follow-up appointments
because monitoring of visual status and prompt intervention of postoperative complications enhance good visual outcome.
activities to avoid
Avoid lifting, pushing, or pulling objects heavier than 15 pounds.
Be careful when climbing or descending stairs.
Avoid bending or stooping
recognition of complications
change in amount or type of eye drainage
redness, swelling or increased pain near the eye
vision change, continuous flashing lights appear to the affected eye
education about medications
Maxitrol drops
used to treat conditions involving swelling (inflammation) of the eyes and to treat or prevent bacterial eye infections.
Antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, and corticosteroid eye drops or ointments
monitored for possible increases in IOP
paracetamol analgesic can be used as PRN for pain
education about eye protection
Keep activity light (e.g., walking, reading, watching television).
Avoid lying on the side of the affected eye the night after surgery.
Clean postoperative eye with a clean tissue; wipe the closed eye with a single gesture from the inner canthus outward.
Always wash hands before touching or cleaning
Wear glasses or eye shield following surgery
Sunglasses should be worn while outdoors during the day because the eye is sensitive to light.
followed by eyeglasses worn during the day and an eye shield at night.
To prevent accidental rubbing or poking of the eye, the patient wears a protective eye patch for about the first 24 hours after surgery
pre-operative care
education about eye medications (antibiotic, corticosteroid, and anti-inflammatory drops) that will need to be self-administered to prevent postoperative infection and inflammation.
Dilating drops are given
ask patients about a history of taking alpha-antagonists
can interfere with pupil dilation during the surgical procedure, resulting in miosis and iris prolapse and leading to complications
known to cause a condition called intraoperative floppy iris syndrome
pre-operative tests
Medical management
surgical procedures
pre-operative meds
Valium Tab
used to treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and seizures. It is also used to relieve muscle spasms and to provide sedation
Atropine drops
used to dilate the pupil before eye exams or surgeries
Gentamycin drops
antibiotics used to prevent eye infections, used pre and post operatively
Lens Replacement
Intra Ocular Lens Implant (IOL)
it's contraindicated in some patients with
recurrent uveitis, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, neovascular glaucoma, or rubeosis iridis.
has low complications
Insertion of IOLs during cataract surgery is the most common approach to lens replacement
Phacoemulsification
a type of eye surgery in which the lens of the eyes are removed
method of extracapsular cataract surgery
Extra Capsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE)
When both eyes have cataracts, one eye is treated first, with at least several weeks, preferably months, separating the two procedures
the delay for the other eye gives time for the patient and the surgeon to evaluate whether the results from the first surgery are adequate to preclude the need for a second operation. The delay also provides time for the first eye to recover; if there are any complications, the surgeon may decide to perform the second procedure differently.
surgery may not be needed
if cataract does not interfere with normal activities
prevention
wear sunglasses outdoors to prevent early cataract formation
optimal blood sugar control for patients with diabetes
weight reduction
smoking cessation
Assessment and Diagnostic findings
tests used to establish the degree of cataract formation
slit-lamp biomicroscopic examination
ophthalmoscopy
absence of red reflex
The Snellen visual acuity test
used to measure the visual impairment.
Clinical manifestations
Light scattering
astigmatism
refractive error due to an irregularity in the curvature of the cornea
reduced contrast sensitivity, sensitivity to glare, and reduced visual acuity.
Painless, blurry vision
Risk factors
Systemic Diseases and Syndromes
diabetes , down syndrome and renal disorders
Physical Factors
trauma or dehydration
Nutritional Factors
obesity and poor nutrition
Toxic Factors
Ionizing radiation
corticosteroids
smoking
Calcium, copper, iron, gold, silver, and mercury, which tend to deposit in the pupillary area of the lens
Alkaline chemical eye burns, aspirin use,
Associated Ocular Conditions
infections and myopia
aging
breakdown of lens protein and low Vit C
What is it?
Cataracts are a leading cause of blindness in the world
a lens opacity or cloudines