realizată de Jaymie Burgess 6 ani în urmă
120
bjaymie@y7mail.com
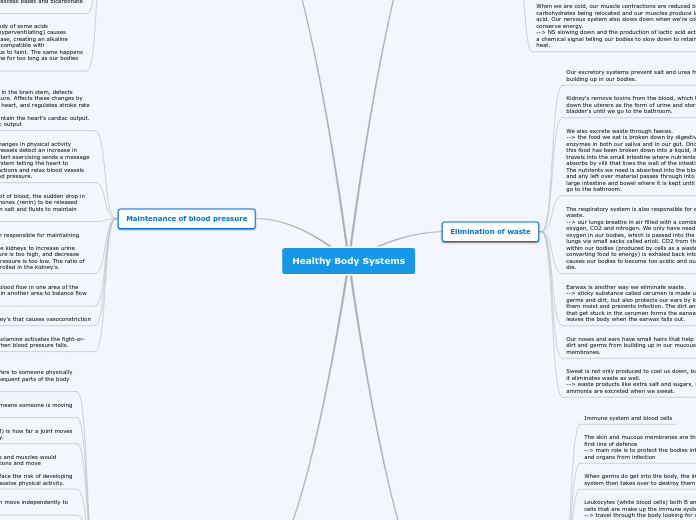
The body maintains blood pressure through a complex interaction involving the cardiovascular center in the brain, which detects changes in pH and blood pressure and sends nerve impulses to the heart to regulate stroke rate and cardiac output.