Methods of Dechlorination
Sulfur Dioxide/Sulfite Salts
L-Ascorbic Acid
Hydrogen Peroxide
Activated Carbon
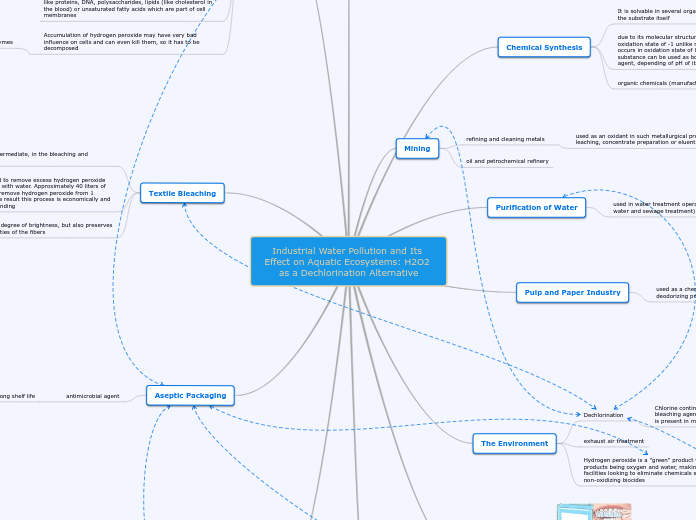
Industrial Water Pollution and Its Effect on Aquatic Ecosystems: H2O2 as a Dechlorination Alternative
Manufacturing of Detergent Bleaches
clothing bleach
produce sodium perborate and sodium percarbonate (bleaching agents in solid and liquid detergents)
Food Processing Industry
Pasteurization was the traditional method used to eliminate substances including hydrogen peroxide which compromise the taste of a variety of milk products. However, it involved the use of heat; this was problematic as many other enzymes that enhance final flavor of the product were denatured. As a result, catalase is now used in the production process in order to convert hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas without affecting the final product. In addition, hydrogen peroxide prevents the growth of bacterial cultures that are beneficial in the cheese production process. Therefore, it is critical that all traces of hydrogen peroxide be removed.
helps to control viscosity of starch and cellulose derivatives
applied in bleaching, oxidizing and neutralizing (in wine distillation) processes
Aseptic Packaging
antimicrobial agent
long shelf life
Textile Bleaching
allows not only a high degree of brightness, but also preserves the mechanical properties of the fibers
The traditional method to remove excess hydrogen peroxide was to rinse the fabric with water. Approximately 40 liters of water are required to remove hydrogen peroxide from 1 kilogram of fabric, as a result this process is economically and environmentally demanding
Medical
Accumulation of hydrogen peroxide may have very bad influence on cells and can even kill them, so it has to be decomposed
reactions in cells are mostly accelerated by enzymes
Catalase lowers the energy of activation needed for decomposition
can have significant impact on aging processes; during decomposition of hydrogen peroxide with, for example, copper (I) and iron (II) ions as a catalyst, hydroxyl radical (OH●) is formed. Free radicals are molecules, atoms or ions which have single, unpaired electron at the outer orbits. High activity individuals have this chemical and oxidize each compound with which they have contact in order to join or donate electrons. The objects of the attacks of free radicals in the human body are mainly compounds having double bonds in the molecules like proteins, DNA, polysaccharides, lipids (like cholesterol in the blood) or unsaturated fatty acids which are part of cell membranes
Hydrogen peroxide could also be found in exhaled air of living organisms. It is uncertain whether the source of it is oral bacteria, phagocytes or other lung cells. People with lung diseases or cigarette smokers exhale more hydrogen peroxide than healthy ones
Hydrogen peroxide naturally occurs in the human body as one of the by-products of biochemical metabolism of many different cells
High reactivity gives H2O2 the ability to damage cellular macromolecules, including lipids, proteins and nucleic acids
Cosmetics
hair bleach
tooth whitening
The Environment
Hydrogen peroxide is a "green" product with the only by-products being oxygen and water, making it desirable for facilities looking to eliminate chemicals such as bleach and non-oxidizing biocides
exhaust air treatment
Dechlorination
Chlorine continues to be used throughout industry as a bleaching agent, a disinfectant, and an oxidizer. As a result, it is present in many industrial and municipal wastewaters
chlorine residuals, even at very low levels, are toxic to certain fish and other aquatic life
Pulp and Paper Industry
used as a chemical intermediate, in the bleaching and deodorizing processes
ncreases brightness levels, improves brightness stability, and reduces manufacturing cost, as it is the only one chemical that is required
Purification of Water
used in water treatment operations (substitute for chlorine in water and sewage treatment)
Mining
oil and petrochemical refinery
refining and cleaning metals
used as an oxidant in such metallurgical process steps as ore leaching, concentrate preparation or eluent treatment
simplifies management of chemicals or waste and improves the overall process control
Chemical Synthesis
organic chemicals (manufacture of glycerol)
due to its molecular structure, it consists atoms of oxygen in oxidation state of -1 unlike many substances, where oxygen occurs in oxidation state of 0 or -2. This means that this substance can be used as both an oxidizing and a reducing agent, depending of pH of its solution.
It is solvable in several organic solvents including water and the substrate itself
Pharmaceutical
One common contact lens disinfectant includes hydrogen peroxide, which oxidizes and cleans the lens. Since hydrogen peroxide is dangerous to the cells of the body, it must be removed. First contact lenses are placed in a hydrogen peroxide containing solution and then placed into a second container, which contains catalases
Hospitals and other healthcare systems find hydrogen peroxide ideal for sanitizing and disinfecting rooms,