realizată de Corinne Nuai 4 ani în urmă
495
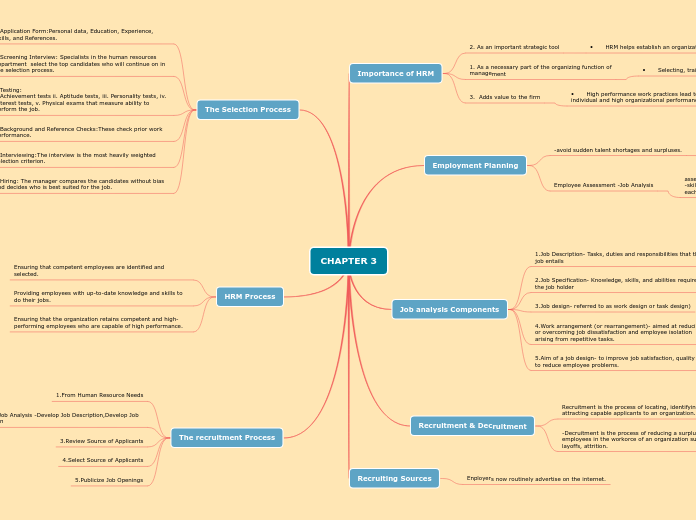
CHAPTER 3
Organizations employ various techniques to design jobs that keep employees engaged and motivated. Job rotation allows employees to work in different departments, gaining diverse experiences.
realizată de Corinne Nuai 4 ani în urmă
495

Mai multe ca aceasta