realizată de Kelly Science 2 ani în urmă
223
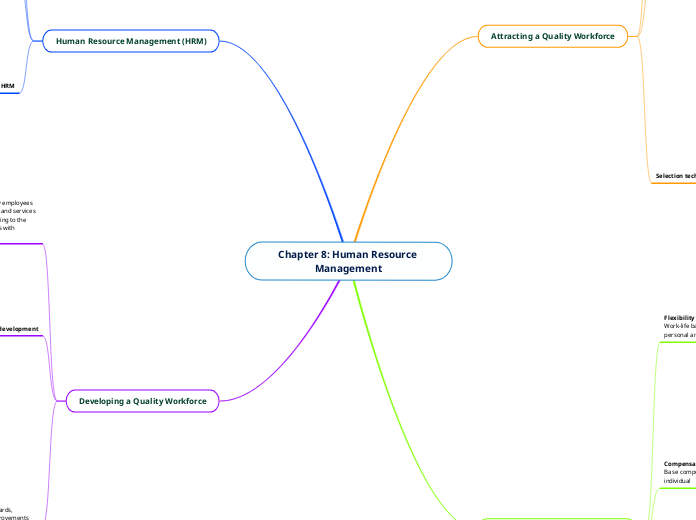
Chapter 8: Human Resource Management
The chapter on Human Resource Management (HRM) delves into the multifaceted process of attracting, developing, and maintaining a high-quality workforce. It outlines the legal environment surrounding HRM, highlighting issues such as sexual harassment, comparable worth, pregnancy discrimination, and the use of independent contractors.