Floating topic
d
CAROL DWECK
ROD ELLIS
The Importance of focus on form in communicative language teaching (2015)
Focus on form
Strategies for doing focus focus-on-form
Reactive focus-on-form
Feedback
Explicit
Implicit
Negotiation
Didactic
Conversational
2 types of focus on form
Pre-emptive
When teacher/student make linguistic form the topic of the discourse even though no error has been committed
Reactive
When teacher/another student responds to an error that a student makes in context of communicative activity
Criterial features
transitory
Occurs in discourse primarily meaning-centred
Arises Incidentally
Observable
attention to linguistic elements as they rise incidentally in lessons whose overriding focus is on meaning
Second Language Acquisition & Language Pedagogy (1992)
Principles of instructed language learning (2004)
CONCLUSION
Computational modal
take for example what is happening in a computer
doesn't work
behaviorism
Why?
important
Principle 10: In assessing learners’ L2 proficiency it is important to examine free as well as controlled production
Measurement
Spot the difference tasks
how many differences spotted = assessment
control practice and free practice
communicative tasks
gap filling exercises
metalinguistic judgement
assessing pupils
being nice to pupils => to keep MFL for GCSE
Principle 9: Instruction needs to take account of individual differences in learners
different learning styles
association
how to maintain and develop motivation?
teacher has to work on intrinsic motivation
escape games
/!/ bribery
DIFFERENTIATION
adaptive teaching
Principle 8: The opportunity to interact in the L2 is central to developing L2 proficiency
groupwork = heterogeneity group
Tolerance to noise = not very frenchy
Use of L1
give role to pupils
scriber
teacher forms groups
IRF
teacher makes assertion
- pupil speaks
- feedback
=> NOT ENOUGH
Johnson
4 parametres
Sujet secondaire
opportunity with personal interaction
Linguistic context where pupil needs to speak
Interaction hypothesis (1996)
props, scaffolding help to interact
Principle 7: Successful instructed language learning requires opportunities for output
TASKS
OUTPUT MORE developed
ORAL presentation
production of output extremely important
pupils can develop their discourse skills
develop own voice/personality
develop their personal discourse
enhance existing knowledge
pupil can try
stimulus response = positive response
Force syntaxic process
Teacher feedback
Principle 6: Successful instructed language learning requires extensive L2 input
how to put in place a good input
create opportunities for pupil to receive a good input outside the classroom
clubs
photography
Photolanguage?
take pictures of the city
Say why has taken this picture?
sport
CUMBRIA METHOD = French in action
=> gestual associated with language
culinary
trips
immersive classroom
Maximise L2 use in classroom
KRASHEN
JUST LIKE ZPD
to progress, input has to be adapted (contextualisation, help)
exemple : authentic ressources -> with help
comprehensible input
Takes time to acquire their L1
exposition to input
more exposition = more acquisition
INPUT has to be very important
Principle 5: Instruction needs to take into account the learner’s ‘built-in syllabus’
Built in syllabus taking into account the pupil
explicit knowledge
don't really know what the pupil has acquired implicitly
grammatical and cognitive complexity
anticipating the pupils development
Zero grammar approach
For Krashen
what we teach isn't what the pupils will acquire
BOITE NOIRE DE CHOMSKY
INPUT
immersive teaching is the only thing that works
/o grammar for him
Selon corder = natural built in syllabus
=> pupils have own natural built in syllabus to learn a MFL
SAME NATURAL ORDER FOR ALL PUPILS?
Principle 4: Instruction needs to be predominantly directed at developing implicit knowledge of the L2 while not neglecting explicit knowledge
Recasting student's utterance in confirmation request
e
IMPORTANCE OF NOTICING ACTIVITIES
Principle 2: Instruction needs to ensure that learners focus predominantly on meaning
WHY TBLT
WHY USING FOCUS ON MEANING?
more effective for fluency
Decoding/encoding activities help with communicative skills
Motivation
Focus on meaning
pragmatical
CONTEXTUALISED, within act of communication
Semantic
GRAMMAR, lexical meaning of a word
Principle 1: Instruction needs to ensure that learners develop both a rich repertoire of formulaic expressions and a rule-based competence
notional functional approach?
helps with working with Notion langagière from chunks
Threshold level
=> COMMUNICATIVE APPROACH
Formulaic expressions
used in everyday life
even used by native speakers
VEE HARRIS
Making boys make progress (1998)
Teaching Learners How to Learn. Strategy Training in the ML Classroom (1997)
BERNADETTE HOLMES
NORBERT PACHLER
ANA REDONDO
Mixed ability grouping in Modern Foreign Languages teaching
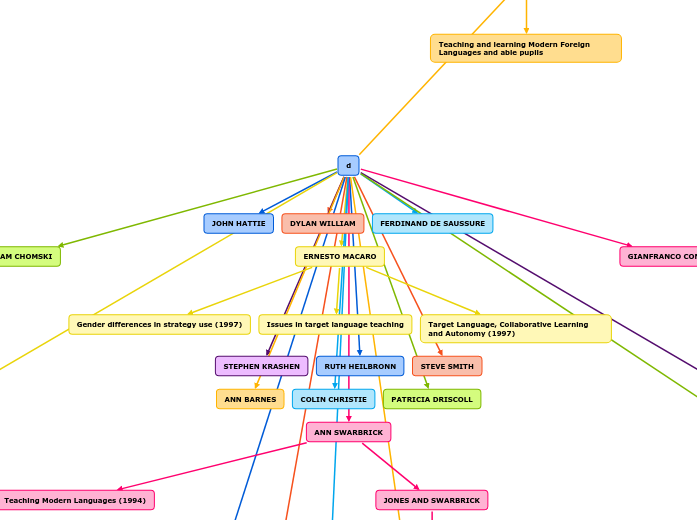
ANN SWARBRICK
JONES AND SWARBRICK
It makes you think, 2004
characteristics of creative activities
TYPES OF ACTIVITIES
Role play
imaginary beasts
classroom magazine
poems
emotions
element of personal choice in terms of subject matter/interpretation, degree of involvement
strong and individual focus
Teaching Modern Languages (1994)
MICHAEL GRENFELL
Communication : sense and nonsense (1991)
PATRICIA DRISCOLL
COLIN CHRISTIE
ANN BARNES
STEVE SMITH
RUTH HEILBRONN
STEPHEN KRASHEN
GIANFRANCO CONTI
ERNESTO MACARO
Target Language, Collaborative Learning and Autonomy (1997)
Issues in target language teaching
Gender differences in strategy use (1997)
NOAM CHOMSKI
FERDINAND DE SAUSSURE
JANE JONES
Teaching and learning Modern Foreign Languages and able pupils
Teaching Grammar in the Modern Foreign Language Classroom
DYLAN WILLIAM
JOHN HATTIE