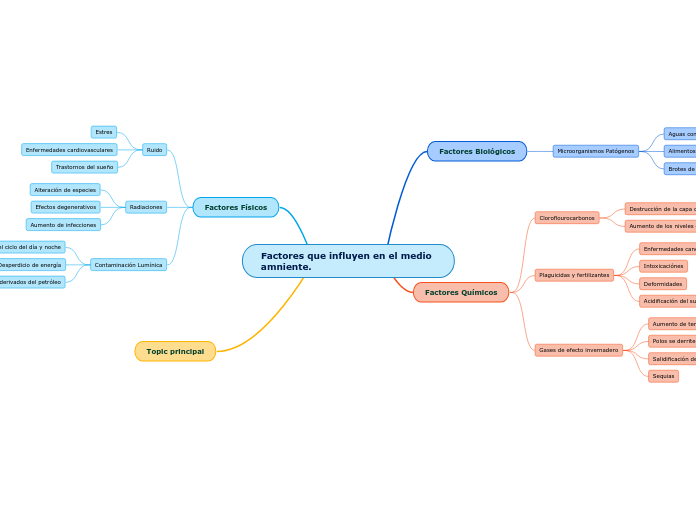
Factores que influyen en el medio amniente.
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
Topic principal
Factores Físicos
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Contaminación Lumínica
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
Aumento del uso de derivados del petróleo
Desperdicio de energía
Alteración del ciclo del día y noche
Radiaciones
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
Aumento de infecciones
Efectos degenerativos
Alteración de especies
Ruido
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Trastornos del sueño
Enfermedades cardiovasculares
Estres
Factores Químicos
Gases de efecto invernadero
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the red car.
Sequias
Salidificación del agua
Polos se derriten
Aumento de temperaturas
Plaguicidas y fertilizantes
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
Acidificación del suelo
Deformidades
Intoxicaciónes
Enfermedades cancerígenas
Cloroflourocarbonos
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
Aumento de los niveles de radiación
Destrucción de la capa de ozono
Factores Biológicos
Microorganismos Patógenos
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
Brotes de enfermedades infecciosas
Alimentos en mal estado
The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed.
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.
Aguas contaminadas
The direct object is the receiver of the action mentioned in the sentence.
Add example