realizată de Juan Carlos CARRENO PARRA 3 ani în urmă
154
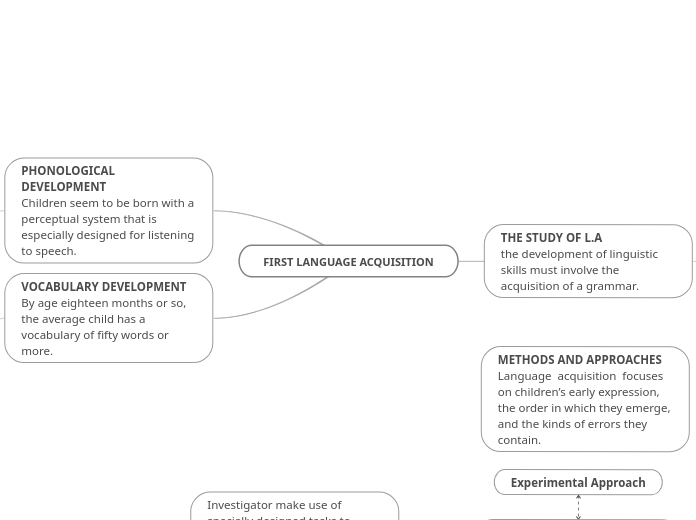
FIRST LANGUAGE ACQUISITION-
Research on language acquisition often involves both naturalistic and experimental approaches to understand how children develop linguistic skills over time. Longitudinal studies, which observe children over extended periods, provide insights into language development by tracking changes and progress.