Hidróxido +Ácido Oxácido →Sal Oxisal+H2O
Metal + Ácido Oxácido→ Sal Oxisal+H2
grupo 1→OH→solubleo oxidacion(II)→menos solubles Oxidacion mayor →insolubles
ECUACIÓN Al^+3 →Al(OH)3
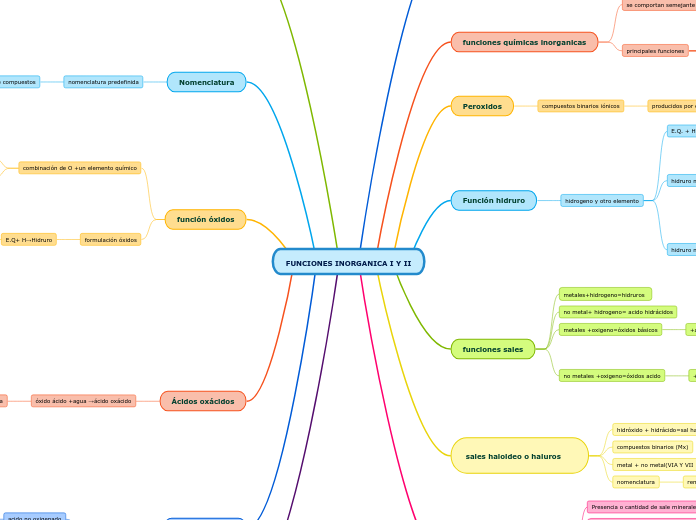
FUNCIONES INORGANICA I Y II
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
sales oxisales
Si el metal presenta dos E.O se utiliza sufijos “oso” e “ico”
Los sufijos “oso” e “ico” del ácido se cambian por los sufijos “ito” y “ato”
enlace iónico: catión(base)-anión(base)
compuestos terciarios(MXO)
según su acido
sales haloideas
acido oxinado
acido oxácido
acido no oxigenado
acido hidracido
Ácidos oxácidos
óxido ácido +agua →ácido oxácido
TRADICIONAL
se nombra
indicando la valencia
4° acido hipo..oso
3° acido hipo...oso
2° acido..oso
1° acido...ico
seguido la raiz del elemento no metal
palabra acido
SISTEMATICA
finalmente añadimos la palabra "de hidrogeno"
en números romanos la valencia
la raíz no metálico acaba en ato
seguido el numero de átomos del elemento no metálico
N° de oxigeno seguido la palabra " OXO"
función óxidos
formulación óxidos
E.Q+ H→Hidruro
n° de valencia
3° valor es TRI
2° valor es DI
1° valor es MONO
es igual para
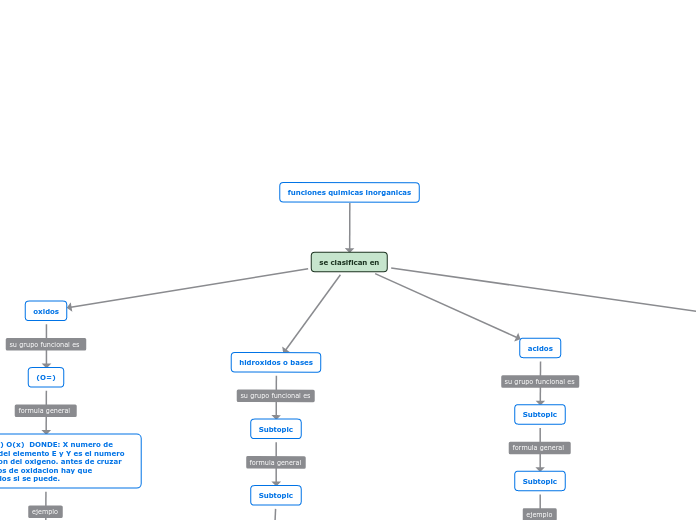
ácidos
basicos
combinación de O +un elemento químico
óxidos ácidos
combinación de un O y un no metal
óxidos básicos
combinación del O y un metal
Nomenclatura
nomenclatura predefinida
3 nombres de compuestos
los sistemáticos IUPAC
revisa y actualiza las reglas
Indica la naturaleza de una sustancia
2° la naturaleza de las especies implicadas
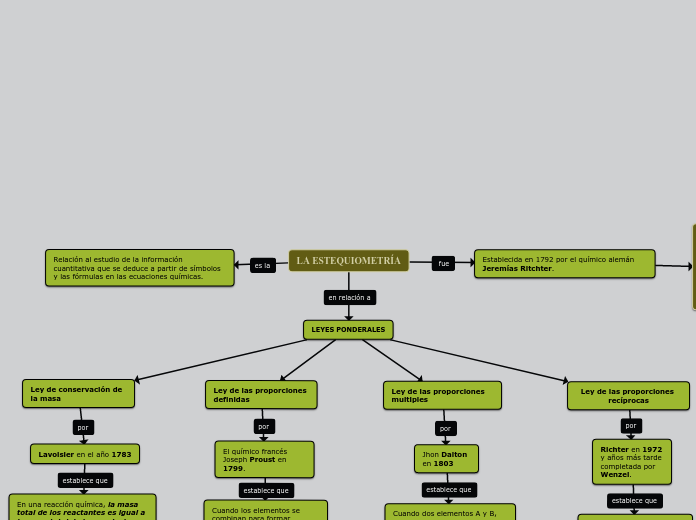
1° la estequiometria
los funcionarios
combinación de palabras
2° nombre especifico
1° nombre genérico
Los vulgares
Hacen referencia a la etimología
Estado de oxidación
numero de oxidación
Solar energy begins with the sun. Solar panels are used to convert light from the sun, which is composed of particles of energy called 'photons', into electricity that can be used to power electrical loads.
Write down the benefits of using solar panels.
REGLAS
Toda molécula simple o compuesta es 0
N.O. de H al combinarse es +1y del O es -2
N.O. de todo átomo sin combinación es 0
Representa carga real
numero de valencia
Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel burned with oxygen.
It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines.
Name the advantages and disadvantages of Hydrogen fuel.
siempre es un numero entero
cantidad de electrones
salinidad de los suelos
tipos de suelos
Suelos Salinos- sódicos
Suelos Sódicos
Suelos Salinos
tipos de sales
Sales no solubles (sulfatos, fosfatos, carbonatos y bicarbonatos
Sales solubles (cloruros)
Proceso de aumento, ganancia o acumulación de sales en el suelo; de origen natural y antrópico.
Presencia o cantidad de sale minerales presentes en el suelo.
sales haloideo o haluros
remplazamos "uro" por "ico" si tiene E.O.→"oso""ico"
metal + no metal(VIA Y VII
compuestos binarios (Mx)
hidróxido + hidrácido=sal haloidea +H2O
funciones sales
no metales +oxigeno=óxidos acido
+agua =oxácidos acido
sal+agua=oxisal
sales dobles
sales basicas
sales acidas
sales neutras
metales +oxigeno=óxidos básicos
+agua=hidróxidos
no metal+ hidrogeno= acido hidrácidos
metales+hidrogeno=hidruros
Función hidruro
hidrogeno y otro elemento
hidruro no metálico
Grupo VIIA Y VIA
Tratadas en función acido
se forma del hidrogeno y un no metal
N.M.+ H→ hidruro
hidruro metálico
Hidrogeno actúa con E.O. -1 cuando se junta con un metal
nomenclatura
3° TRI
2° DI
1° hidruro
E.Q. + H →hidruro
Peroxidos
compuestos binarios iónicos
producidos por el grupo IA y IIA
funciones químicas inorganicas
principales funciones
sal
hidroxido
hidruro
oxido
se comportan semejante por su grupo funcional
hidroxidos
There are many different types of energy, which all fall into two primary forms – kinetic and potential.
Energy can transform from one type to another, but it can never be destroyed or created.
compuesto ionico
Gravitational energy is a form of potential energy.
It is energy associated with gravity or gravitational force, in other words, the energy held by an object when it is in a high position compared to a lower position.
Give examples.
no metal como anion (OH)^-1
metal como cation
metal alcalino y alcalinoterreo
Nuclear energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms.
This energy is released when the nuclei are combined (fusion) or split apart (fission).
Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms to produce electricity.
What element do they use to fuel nuclear power plants?
metal+H2O→hidroxido+H2
grupo funcional oxidrilo y hidroxilo
Thermal energy is created from the vibration of atoms and molecules within substances. The faster they move, the more energy they possess and the hotter they become. Thermal energy is also called heat energy.
Give examples of heat energy.
oxido agua=hidróxido
compuestos ternarios
Motion energy or mechanical energy is the energy stored in objects; as objects move faster, more energy is stored.
Examples of motion energy include wind, a flowing river, etc.
Give more examples.
Example