PHASES OF REHABILITATION
INJURY PROGRESSION STRATEGIES
STRATEGIES STAGES 1
STRATEGIES STAGES 2
STRATEGIES STAGE 3
STRATEGIES STATE 4
STRATEGIES STATE 6
the work on the range of movement may prevent other issues, such as a calf muscle tear
Movements that test and train proprioception and coordination must be diverse, challenging, entertaining, and relevant to the person’s future activity
Repeated concentric loading at a certain speed can be accurately measured with an isokinetic machine
estimularse a través de movimientos pasivos y activos de las articulaciones y tejidos blandos
Knowledge of range of movement before injury is beneficial, which is why annual musculoskeletal screening/profiling is beneficial in sport
Aquatic therapy is an excellent modality to ease swelling and pain because of the compressive effect of water and the beneficial effect of minimal movement in deep water.
Gentle active resisted muscle activation is possible at this stage.and can be induced by electrical activation, to avoid the muscle-damaging effect of pain and swelling
Analgesia has its place at this stage to decrease inflammation and allow the patient to become more mobile and, importantly, adopt as normal a gait as possible as early as possible
PHASE
PHASE 7: RETURN TO PLAY
he decision to return to play can be the doctor (who determines that the clinical evaluation shows that the patient is continuing to improve and can sustain increased load
PHASE 6: RETURN TO FULL TRAINING WITH PREVENTION
6. Understanding self-management strategies Another example could be a professional football player recovering from the sameoperation, for whom the criteria may be
7. Ability to manage striking a ball and endurance work on the grass for up to time
spent in a normal training session
1. Maximal joint range compared with the other side/preinjury range.
2. No pain or swelling.
3. Maximal isotonic/isokinetic power of lower leg musculature
4.Maximal jump test compared with previous measures (compare left vs. right)
5. Ability to perform hop-and-hold test with maximal proprioception/agility
6. Attain preinjury levels of number and quality of maximal accelerations and deceler- ations comparing right and left sides
PHASE 5: ACHIEVE PREVIOUS LEVELS OF SKILL AND AGILITY
Patients and players may now be under pressure to return to full activity because
they are seen to be functioning at a high level
INJURY PROTOCOLS
1. No ankle swelling or pain and good range of movement
2.Test shows good cardiovascular endurance compared with previous testing
3. Basic proprioception and coordination in the water, sand, trampoline, and grass,
showing symmetry
4.1. Perform tasks relating to the sport, such as kicking, jumping, twisting, sprinting, and tackling
5.2 . Perform these tasks with increasing load, such as with a heavier ball, greater speed of movement,
PHASE 4: ACHIEVE TO LEVELS OF PROPRIOCEPTION AND COORDINATION
understanding human nature, the practitioner may wish
to introduce aspects of phase 5
objetico Using the discipline of balance, proprioception and coordination in a variety of ways to enable the patient to master body control, can be rewarding.
PHASE 3: ACHIEVE FULL POWER AND ENDURANCE
OBETIVO
Isometric and isotonic exercise are inexpensive and easy to
perform as a self-management process, and can be performed with the joint isolated
effort or exercise to fatigue (can the patient perform 10 lunges, for example) using scien- tific laboratory–based assessment and field testing of functional movement patterns.
PHASE 2: ACHIEVE FULL RANGE OF MOVEMENT AND FLEXIBILITY
OBJETIVO
The range of motion of the joints and contractile tissues involved (proximal and distal to the lesion) should be stimulated as soon as possible.
PHASE 1 DECREASE THE PAIN AND SWELLING
OBJETIVO
Many methods are available to alleviate swelling; however, compression, cooling, and elevation seem to be the mainstays of treatment.
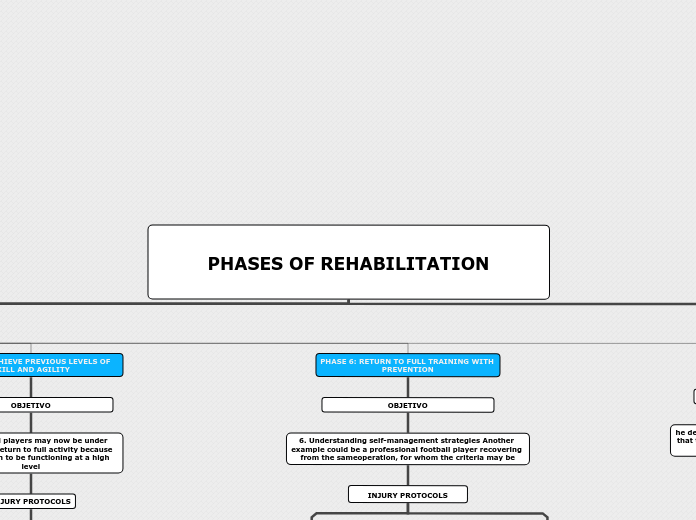
REHABILITATION CAN FALL INTO 7 CATEGORIES
1.Decrease pain and swelling.
2.Achieve full range of movement and flexibility.
3.Achieve full power and endurance.
4.Achieve top levels of proprioception and coordination.
5. Achieve previous level of agility and skill.
6.Return to full training, with prevention.
7. Return to play.