1) When circular muscles contract longtitudinal muscles relax 2) When circular muscles relax longtitudinal muscles relax
2) Wall Dillates = Food can enter
1) Wall Constricts = Food Pushed
Hepatic portal vein
Breakdown large molecules in food into small soluble molecules to be absorbed.
Increse surface area to volume ratio so that digestive enzymes can act on food more efficiently.
Human Nutrition
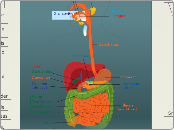
Organs and glands associated with the gut
Pancreas
Produce hormones
Insulin and Glucagon
Produce pancratic juice.
Gall Bladder
Temporarily store bile
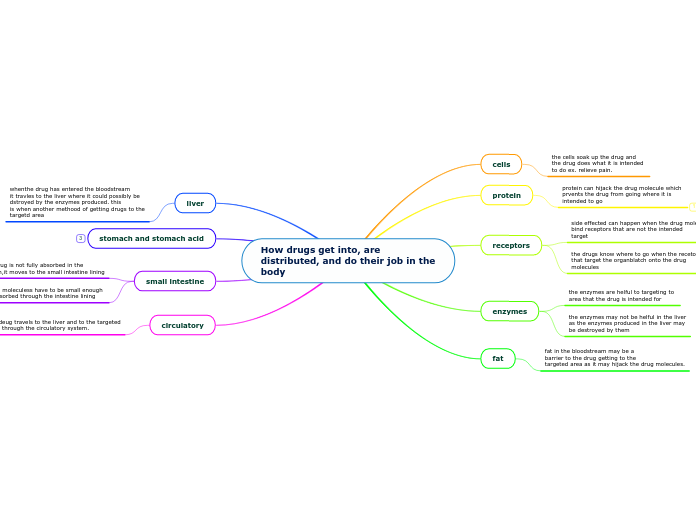
Liver
Detoxification of alcohol
Alcohol dehydrogenase break down alcohol to form acetaldehyde which may be used in cellular respiration.
Deamination of amino acids
Protein Synthesis
Break down haemoglabin in red blood cells
Regulate blood glucose concentration
Aid in fat digestion by secreting bile
Bile emulsifies fats
Alimentary Canal
Anus
Faces are egeested through the anus.
Large intestine
Colon Rectum
-Water and mineral salts are absorbed from undigested food material. -Faces are stored temporarily in the rectum.
Small Intestine
Ileum
- The small intestine is long to provide sufficient time for absorption. - The intestinal wall and the villi have many capillaries to carry away the absorbed food substances. In each villus is a lacteal or lymphatic capillary surrounded by blood capillaries. This continual transport of digested food substances maintains the concentration gradient for the absorption of digested food substances.
- The inner wall of the small intestine is highly folded. - The folds are lined with microscopic, finger-like projection called villi. - The epithelial cells of the villi, in turn, have numerous microvilli. - The epithelium of the villi is one cell thick.
Increases surface area to volume ratio for absorption
Digested food are absorbed by the villi of the small intestine.
Glycerol and fatty acids diffuse into the epithelium, where they recombine to formfat globules and enter lymphatic capillaries.
Glucose and amino acids are absorbed by diffusion/active transport into the blood capillaries.
Duodenum
Physical Digeation
Bile salts emulsify fats into tiny droplets.
Chemical Digestion
Pancreas secrete pancreatic juice - Action of amylase : starch ------>maltose - Action of trypsin : starch ------>maltose - Action of lipase : fats ------>fatty acids and glycerol
Intestinal glands secrete intestinal juice - Action of enterokinase : trypsinogen ------> trypsin - Action of maltase : maltose ------>glucose - Action of lactase : lactose ------> glucose and galactose - Action of sucrase : sucrose ------> glucose and fructose - Action of erepsin : polypeptides ------> amino acids - Action of lipase : fats ------> fatty acids and glycerol
Stomach
Chemical Digestion
Action of rennin : soluble caseinogen ------> insoluble casein
Action of pepsin : proteins ------> polypeptides
Physical Digestion
Peristalsis mixes the food with the gastric juice
Oesophagus
Food passes down via peristalsis by antagonistic muscles
Longitudinal muscles (outer layer)
Circular muscles (inner layer)
Mouth
Chemical Digestion
Action of salivary amylase : strach ------> maltose
Physical Digestion
2) Tongue mix food and rolls food bvvinto small round masses (boli)
1) Chewing break up the food.