realizată de Moses Aidoo 4 ani în urmă
305
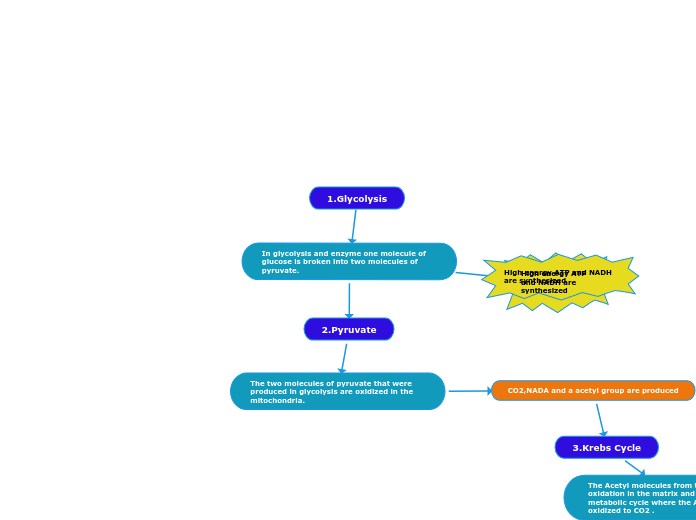
In glycolysis and enzyme one molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate.
The process of cellular respiration involves several key steps to convert glucose into usable energy. Initially, glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, where one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, yielding a small amount of ATP and NADH.