LA BASILICATA
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
Ramo principale
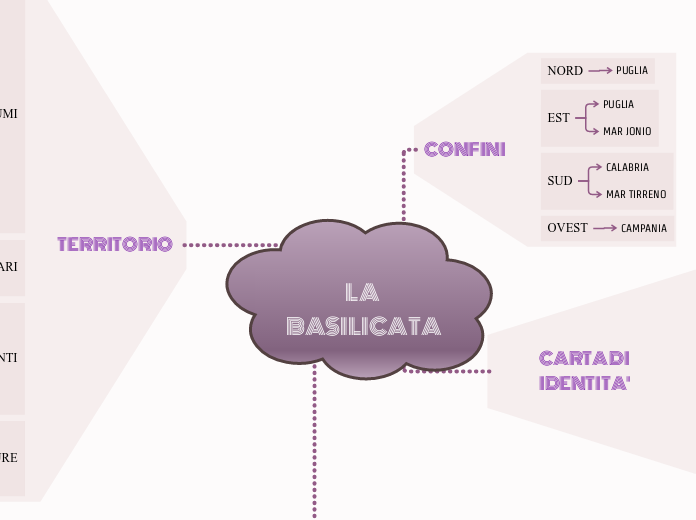
TERRITORIO
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
COLLINE E PIANURE
PIANURE
PIANA DI METAPONTO
COLLINE
A EST DELL'APPENNINO LUCANO FINO ALLA COSTA
MONTI
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will be finished by a particular time in the future
- an action that starts before and continues up to another action or time in the future
- an action that will finish before a certain time in the future, but it is not known exactly when
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow by 7)
APPENNINO LUCANO
Structure:
Subject + Will Have + Past Participle
e.g. I will have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
MONTE VULTURE 1326 m
MONTE VOLTURINO 1835 m
MONTE SIRINO 2005 m
MONTE POLLINO DI 2267 m
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will have beenYou will have beenHe/She/It will have beenWe will have beenYou will have beenThey will have been
Form of verb 'to have':
I will have hadYou will have hadHe/She/It will have hadWe will have hadYou will have hadThey will have had
MARI
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
Structure:
Will + Subject + Be +Verb-ING?
e.g. Will you be having fun at the party?
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
LAGHI E FIUMI
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
FIUMI
'Going to' Future is used:
- to talk about our future intentions and plans
- for commands
Some adverbs used with 'Going to' Future:
- later
- tonight
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
SINNI
AGRI
Structure:
BE + Subject + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb?
e.g. Are you going to read the whole book over the weekend?
BASENTO
Structure:
Subject + BE not + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. He isn't going to spend his vacation in Hawaii.
BRADANO
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. She’s going to be a professional dancer when she grows up.
LAGHI
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
NATURALI
Structure:
Subject + Won’t (will not) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. You won’t see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
ARTIFICIALI
Structure:
Subject + Will + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I will see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
LAGO DI MONTE COTUGNO
LAGO DI PIETRA DEL PERTUSILLO
LAGO DI SAN GIULIANO
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will beYou will beHe/She/It will beWe will beYou will beThey will be
Form of verb 'to have':
I will haveYou will haveHe/She/it will haveWe will haveYou will haveThey will have
CARTA DI IDENTITA'
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
IL CAPOLUOGO E LE PROVINCE
Past Perfect Continuous is used:
- for an action that started in the past and continued up to another point in the past
- to show cause and effect
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Continuous:
- since (e.g. since yesterday)
- for (e.g. for 10 years, for 6 months)
PROVINCE
Structure:
Subject + hadn’t been/had not been + Verb-ING
e.g. I was tired because I hadn't been sleeping.
MATERA
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I had not been beingYou had not been beingHe/She/It had not been beingWe had not been beingYou had not been beingThey had not been being
Form of word "to have":
I had not been havingYou had not been havingHe/She/It had not been havingWe had not been havingYou had not been havingThey had not been having
CAPOLUOGO DI PROVINCIA
Structure:
Subject + had been + Verb-ING
e.g. They had been talking for over an hour before I arrived.
POTENZA
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I had been beingYou had been beingHe/She/It had been beingWe had been beingYou had been beingThey had been being
Form of verb 'to have':
I had been havingYou had been havingHe/She/It had been havingWe had been havingYou had been havingThey had been having
DENSITA'
Past Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that began in the past and is still going on at the moment of speaking
- an action that continued before and after another action
- a change of mind
- an action happening repeatedly in the past
The Past Perfect tense is not normally used alone. It is used to denote the earlier of two past actions. We use Past Simple for the latter action.
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Simple:
- already, before, ever, never
- once, twice, yet
- just, up to then
- for, since
59 ABITANTI PER KM²
Structure:
Subject + had + Past Participle
e.g. They had already met Julia before the party.
POPOLAZIONE
Past Continuous is used for:
- an action that happened before another action in the past
- an action that started in the past and continued up to a given time in the past
- an action done several times up to a point in the past and continued to do after that point
- an action that happened in the past but is important at the time of reporting
Some adverbs used with Past Continuous:
- always, only, never, ever, still, just
590512 ABITANTI
Structure:
Subject + was/ were + Verb-ING
e.g. You were studying when she called.
SUPERFICE
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
99992 KM²
Structure:
Subject + Verb in Past Simple (2nd form)
e.g. They lived in Spain three years ago.
CONFINI
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
OVEST
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
CAMPANIA
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
SUD
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
MAR TIRRENO
Structure:
Have/ has +Subject+ Past Participle?
e.g. Has she finished the letter?
CALABRIA
Structure:
Subject + haven’t (have not)/ hasn’t (has not) + Past Participle
e.g. She hasn’t finished the letter.
EST
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
MAR JONIO
Structure:
Subject + BE not + Verb-ING
e.g. You are not eating now.
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
NORD
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
PUGLIA
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.