realizată de Giuseppe Madeo 5 ani în urmă
629
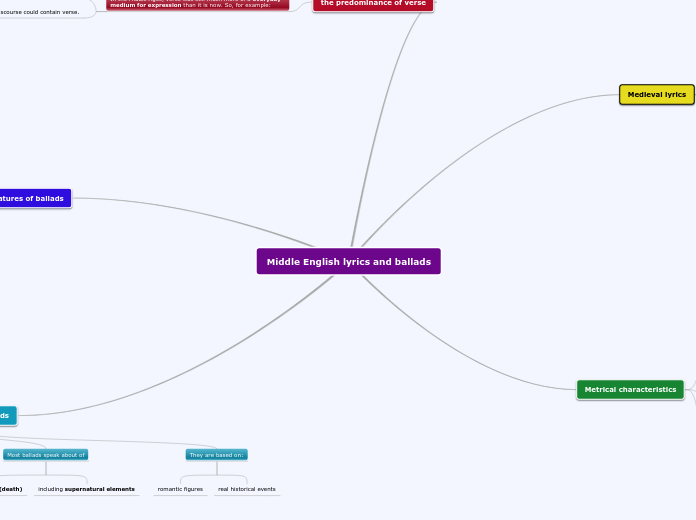
Middle English lyrics and ballads
Medieval romance literature, particularly exemplified by Thomas Malory's "Morte D'Arthur," weaves together stories of knights and the Arthurian legend, presenting a unified narrative from King Arthur'