Political and Economic Factors Affecting International Business
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
Center Wing
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
Past Continuous is used for:
- an action that happened before another action in the past
- an action that started in the past and continued up to a given time in the past
- an action done several times up to a point in the past and continued to do after that point
- an action that happened in the past but is important at the time of reporting
Some adverbs used with Past Continuous:
- always, only, never, ever, still, just
Mixed Economy
Structure:
Was/ were + Verb-ING?
e.g. Were you studying when she called?
Mixed economies have aspects of both market and centrally planned economic systems
Mixed economies merge government engagement with business private ownership
The majority of major industries in socialist mixed economies are government-controlled
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Was I being?Were you being?Was he/she/it being?Were we being?Were you being?Were they being?
Form of word "to have":
Was I having?Were you having?Was he/she/it having?Were we having?Were you having?Were they having?
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
Liberal Democrats (UK)
Structure:
Subject + Verb in Past Simple (2nd form)
e.g. They lived in Spain three years ago.
MoDem (France)
Liberals (CANADA)
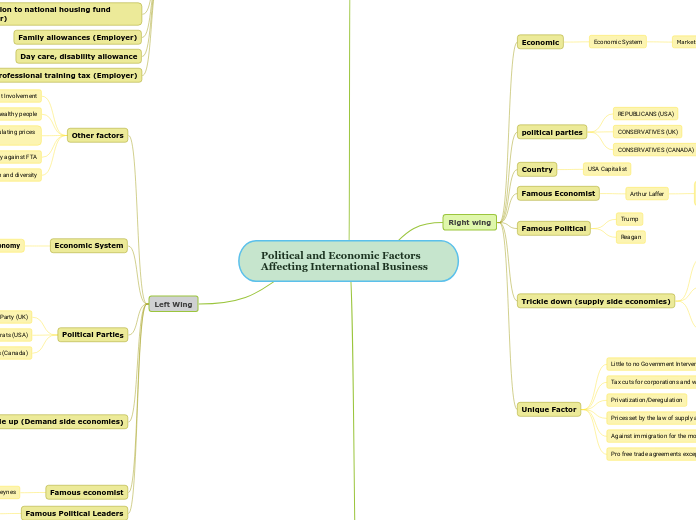
Left Wing
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
Famous Political Leaders
Barak Obama
Famous economist
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will continue up until a point in the future
- an action that finishes just before another time or action in the future
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Continuous for future actions:
- for
- since
- next week
- next month
- next year
John Keynes
An English economist with theories that have transformed macroeconomic practise and policies completely
Trickle up (Demand side economies)
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will be finished by a particular time in the future
- an action that starts before and continues up to another action or time in the future
- an action that will finish before a certain time in the future, but it is not known exactly when
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow by 7)
Government can generate demand for goods and services if people and businesses are unable to
Structure:
Will + Subject + Have + Past Participle?
e.g. Will you have met your colleague by this time tomorrow?
Putting more money in the pockets of the middle and lower classes has a greater benefit to the economy than saving or stockpiling the money in a wealthy person's account. (Taxing corporations and the rich instead of the middle and lower classes)
A important aspect of economic demand is aggregate demand
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Have + Past Participle
e.g. I won’t have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Demand-side economics refer to Keynesian economists' belief that demand for goods and services drive economic activity
Structure:
Subject + Will Have + Past Participle
e.g. I will have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Political Parties
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
New Democrats (Canada)
Structure:
Will + Subject + Be +Verb-ING?
e.g. Will you be having fun at the party?
Democrats (USA)
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
Labour Party (UK)
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
Command Economy
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
The state takes decisions on price and wage regulations, production quotas and raw material distribution
The needs of the whole of society are seen as more important than the needs of the individual
Structure:
Will + Subject + V1(First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Will you see Mary when she comes back from Denmark?
The motive for profit is not the main purpose of the business, as government control is increased
Structure:
Subject + Won’t (will not) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. You won’t see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
The government restricts and controls private land ownership
Structure:
Subject + Will + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I will see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
The government regulates the amount, distribution, and price of goods and services
Other factors
For immigration, inclusion and diversity
Mostly against FTA
more government intervention when it come to regulating prices and owning subsidies
More taxes in Corporations and wealthy people
More Government Involvement
Social security contributions levied on employers
Professional training tax (Employer)
Day care, disability allowance
Family allowances (Employer)
Contribution to national housing fund (Employer)
Medical insurance - Reimbursements for medical and hospital expenses or provision of hospital or medical services - including maternity leave (Employer)
Financing of workers union (Employer)
Old-age, disability and survivors' pensions (Both employer and employee)
Accident and injury insurance (Employer)
Unemployment insurance benefits and supplements (Employer)
Right wing
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Unique Factor
Pro free trade agreements except for far right
Against immigration for the most part
Prices set by the law of supply and demand
Privatization/Deregulation
Tax cuts for corporations and wealthy people
Little to no Government Intervention
Trickle down (supply side economies)
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
President Reagan and his Republican contemporaries popularised the idea that larger tax cuts are creating incentives for wealthy investors and entrepreneurs to save, invest and deliver economic advantages that trickle into an economy as a whole.
Structure:
Have/ has + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long has he been learning German?
Supply-side economics is an economic theory that postulates tax cuts for the wealthy result in increased savings and investment capacity for them that trickle down to the overall economy
Structure:
Subject + haven’t/hasn’t been + Verb-ING
e.g. She hasn’t been playing tennis for a long time.
The argument that supply creates its own demand
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
Famous Political
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
Reagan
Structure:
Have/ has +Subject+ Past Participle?
e.g. Has she finished the letter?
Trump
Structure:
Subject + haven’t (have not)/ hasn’t (has not) + Past Participle
e.g. She hasn’t finished the letter.
Famous Economist
Arthur Laffer
An American economist and a member of Reagan's Advisory Committee on Economic Policy. In addition, in the 2016 Trump presidential race, he was an economic adviser.
Country
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
USA Capitalist
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
political parties
CONSERVATIVES (CANADA)
CONSERVATIVES (UK)
REPUBLICANS (USA)
Economic
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
Economic System
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.
Market Economy
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb "to be":
I amYou areHe/she/it isWe areYou areThey are
Form of verb "to have":
I haveYou haveHe/she/it hasWe haveYou haveThey have
Competition is a healthy and important factor in the development of quality and lower prices.
Global investments are promoted, however self sufficiency is not an economic priority
Private ownership is promoted (including business)
encourages firms to launch new goods that are much better
Prices depend on supply and demand law prices
Governments have little direct business intervention