SCH3U0
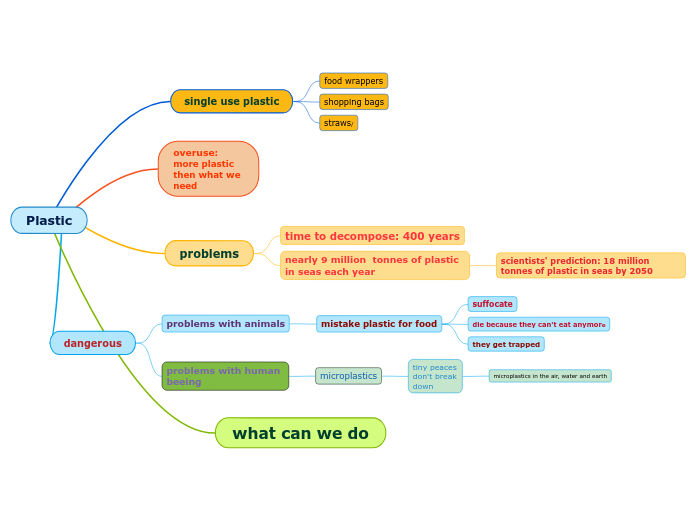
What problem do you want to solve?
Type in the box.
E.g.
I can't save moneyI can't lose weightMy neighbor is very loudI can't quit smokingI don't exercise enough
Quantities In Chemical Reactions
Now it's time to execute your plan.
You can also:
- print this map....
- download it in various formats
Thanks for Mind Mapping!
Units Of Quantity
Molar Mass
How to find it?
The subscript of the atom tells us how many of that particular atom there is
Example= CO
1C(12)+ 1O(16)= 28 g/mol
In a given molecular compound multiply the individual atoms atomic mass with its subscript.
Unit of Measurment= g/mol (grams per mol)
Mass of individual atom or molecular compound
Avogadro's Number
The constant number; unit of measurement as described before
The Mol
The mol is a unit of measurement, this number is specifically used in labs to count molecules, atoms, ions and/or electrons.
How much is a mol?
= 6.02x10^22
1 mol would equal to approximately 26 grams of aluminum
Unit of Measurment= n
Stoichometry
Molecular Formula
Finding the number of individual atoms in the equation.
Empirical Formula
Simplified formula with minimal rations
Stoichiometric Ratio's
Example= 2H2O= 2NO3
The mol:mol ration for O is 2 because they each have 2 moles in front.
Quantities in Chemical Reactions
Excess Reactant
Simply the other reactant which still remains after the completion of the reaction.
Limiting Reactant
The reactant in the equation which will run out first. This is limiting because without this the reaction cannot advance.
Solutions and Solubility
Create a plan of how to solve the problem.
Acids And Bases
pH Scale
Acids are solutions with a pH of under 7 and bases are above 7
A logarithmic scale is used to determine the acidic or basic levels or a solution.
Properties
Base: Also forms electrolytes, produces hydroxide ions in water and tastes bitter.
Acid: Forms electrolytes Produces hydronium ions and they taste sour.
Concentrations
Molar Concentration
Calculated by c= n/V or M= n/V
PPM Concentration
Can be used for quality testing in air quality, metal, plastic parts in food and pollutants in water supplies.
6-9 PPM is considered polluted, First Nations in Canada are now suffering from polluted water sources.
Used to measure miniscule substance concentrations. (PPM= Parts Per Million)
Can also be calculate further using PPB and PPT (Parts Per Billion and Parts Per Trillion). These can be used to trace contaminants in water sources.
Standards
Volume/Volume%
Mass/Volume%
Mass/mass%
The Measurement of how much of a substance is mixed into another substance.
Dilution
Formula: C1V1= C2V2
Making a concentrated substance weaker by diluting it with excess solvent.
Solutions
Components
The solute, substance that dissolves in the solvent
The solvent, substance that dissolves the solute
Characteristics
What actions will you take?
Solute particles can be filtered out. Also, precipitate formed when the mixing occurs is created due to the mixture of positive and negatively charged ions.
A homogenous solution, transparent, aqueous, may be coloured.
What is the expected effect of this action related to your problem?
Gases and Atmospheric Chemistry
This branch will guide you to think about the possible solutions available to your problem.
Molar Volume In Gas Units
STAP
STP
Standard Temperature Pressure
Gas Laws
Ideal Gas Law
Combined Gas Law
Charle's Law
Boyle's Law
Gay-Lussac's Law
Chemical Reactions
To solve your problem 'SCH3U0' you need to establish clear goals of what you want to achieve.
Write down your goals, each goal on a new branch connected to this topic.
Combustion
A combustion reaction can only occur in the presence of oxygen. This reaction when completed is often accompanied by light, heat and sound.
Double-Displacemnt
A double displacement is when the positive and negative ions of a compound are swapped out with the other negative and positive counter parts of the other compound.
Single-Displacement
A single displacement occurs when in the reaction an element needs to be swapped out with another product in the element compound.
Decomposition
Decomposition is the complete opposite of synthesis. The synthesized reactants now break up into their original reactant forms.
Synthesis
What are your goals by solving this problem?
This reaction occurs when reactants (2 or more) react together to form a singular product, hence synthesizing themselves.
What would the ideal situation if this problem would go away?
current situation
Describe the current situation.
Press Enter if you have more answers.
Matter, Chemical Trends and Chemical Bonding
To understand your problem this branch will guide you to:
Describe your problem in detail
Press the next below to continue.
Chemical Bonds
What is the cause of this problem?
Polarity
This can be either negative or positive (polar or nonpolar)
The distribution of electron charge throughout the whole molecule joined at the bonds.
An H2O molecule would be a polar molecule because of the unequal electron charge throughout the bonds. The molecule itself has an unsymmetrical shape.
Covalent Bonds
A covalent bond is the result of 2 non metal atoms sharing electron pairs hence connecting and making a bond.
Ions
Diatomic
Diatomic elements can be classified as molecules with only 2 atoms.
There are 7 total diatominc elements and can be easily memorized using HOFBrINCl
Hydrogen, Oxygen, Flourine, Bromine, Iodine, Nitrogen and Chlorine.
Polyatomic
A polyatomic ion is an ion which consists of more than 3 atoms.
Example: Sulfate Ion
Ionic Bonds
The atom with the valence electron furthest from it's shell gets its electron permantley transfered to the other atom.
The atom losing the electron becomes a positively charged ion and the gaining one becomes negatively charged.
The result of bonding by 2 oppositely charged ions.
Electron Arrangement
Valence Electrons
Diagrams
Lewis Dot Diagram
A Lewis dot diagram is used to show the bond between the atoms of a molecule.
Bohr-Rutherford diagram
The Bohr=Rutherford diagram is used to show the orbiting
electrons of an atoms nucleus.
Atomic Number
This is how the periodic table is determined today.
This number is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of any certain atom.
Periodic Trends
Describe the current situation of the problem.
What is happening now?
Type your answer in the box.
Periodic Table
Reactivity
Reactivity can be explained as how strongly an atom might react with another atom. It's basically an expenditure of energy.
Highly electropositve and electronegative atoms have a high tendancy to react. This may also depend upon temperature.
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius is a measurement found by measuring the size of the atoms from the nucleus to the outermost electron.
Ionization Energy
The more shells an atom has the easier it gets to lose a valence electron as it gets further away from the nucleus and isn't held on as strongly.
Simply put, the ionization energy of an atom is the minimum energy required to lose a valence electron.
Francium has the lowest ionization energy as it has more shells in comparison to Helium which has just one shell.
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to gain more electrons, this varies with atomic number
97 years later a chemist named Henry Moseley rearranged the periodic table
This table was arranged through atomic number and remains this way till now.
Arranged the elements in increasing atomic mass