realizată de Artem Pekun 3 ani în urmă
124
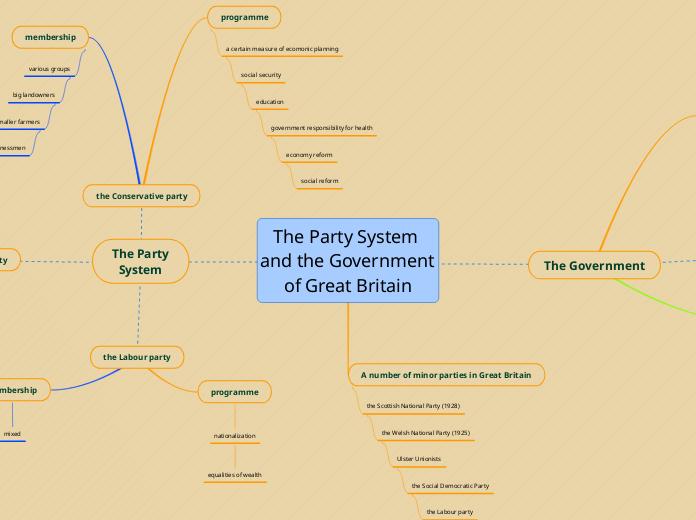
The Party System and the Government of Great Britain
The political landscape of Great Britain is characterized by a diverse array of parties and a structured government system. Among the prominent political entities are the Labour Party, which emphasizes nationalization and equality of wealth, and the Conservative Party, with its focus on economic planning and social reforms.