STUDENT NO : 219127618
Each of these knowledge types can be acquired from experience or even from rational thought. Understanding the connections between the three types of knowledge can be helpful in clearly understanding what is and what is not being analysed by the various theories of knowledge
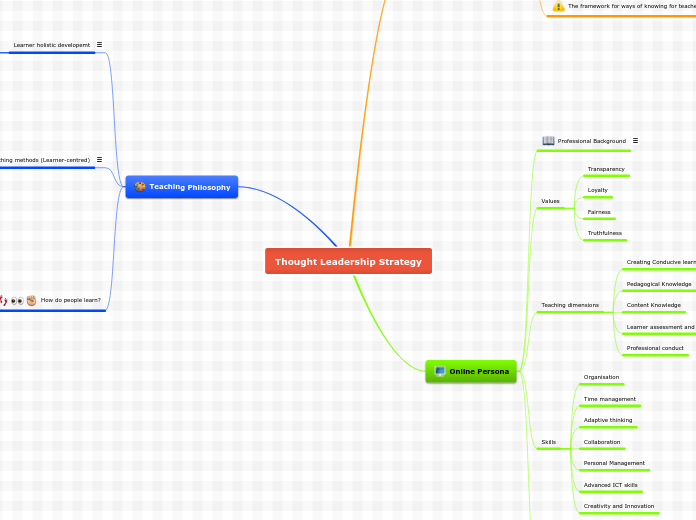
Thought Leadership Strategy
Teaching Philosophy
How do people learn?
Behaviourism
1. In behaviourism, change in behaviour demonstrates that learning has occurred. For example, when the teacher does presentations that produce desired effect, learning thought to happen in response to that stimuli. The response is further reinforced when the outcome is positive and pleasant. In that regard, I personally draw from the behaviourist approach in that I welcome and encourage good practices in the class especially on the issues pertaining to classroom management and learner behaviour. In my opinion, the ideas of positive and negative reinforcement are effective tools of learning and behaviour modification, as well as a punishment and reward system.
Skinner
Progressive Learning theories
My teaching practice embraces the progressive learning theory. The theory which acknowledges Piagent’s ideas on child development, Vygotsky’s ideas about socially situated learning and the construction knowledge, and the on both the experience and cognition as a basis for learning. This theory has led to the establishment of learner-centred schools for students to approach learning through their own personal experiences. It deviated away from the notion that learning occurs through transmission of information by knowledgeable other. Progressive learning theory recognises the role that both experience and self-reflection play in building and organising own knowledge
The theory incorporates the role of cultural beliefs and experience on how people construct their understanding and develop their abilities. Culture influences the knowledge and experiences children bring to the classroom, how they communicate, their expectations and their ideas as to what is worth learning. For instance, some learners may not view evolution as a subject worth learning due to their religious reasons. Progressive learning theory also acknowledges that people learn by making sense of the environment and stimuli around them. Learning involves making connections and drawing conclusions on the sense of what is already known and have been experienced.
Constructivism
Constructivism is the idea that people are responsible in creating their own understanding of the world and using what they know based on previous experiences in the process of linking new information to these experiences. People use these experiences and new information to construct their own meaning. I also employ constructive approaches in the classroom by drawing on learner’s prior knowledge and actually allow learners to be active members who utilise various resources to construct knowledge with or without much assistance from me as teacher.
Vygosky
Vygotsky’s theory is about socially situated learning and the construction knowledge
Piagent
Theory on stages of child development
Doing
experience
What is learning?
Learning : unending pursuit of building knowledge onto own experience
Teaching methods (Learner-centred)
I employ various teaching methods in order to cater for different learning styles thereby reaching out to all learners. Integrating technology in the classroom makes it possible to customise learning for individual learner needs.
I believe that learners learn best through experience and also through hands on activities and therefore I prepare resources for learners to interact with in order to make connections and construct knowledge. I challenge learners to think out the box by asking open ended questions that enable learners to investigate and draw own conclusions based on their findings. I strongly believe that learning is an active process that require learners to be active participants at all times. It is without any doubt that my teaching practice is largely influenced by the constructivist view of learning, however I do believe that positive reinforcement also plays a role in promoting good practices in the classroom.
Gamification
problem based learning
Inquiry based learning
Experiments
Digital technology
Cooperative learning
Learner holistic developemt
Schools should aim at holistic development of the child and not only at intellectual development. I believe that schools should tap into intellectual, emotional, physical and social aspects of a child’s development. I utilise proactive approach to classroom management. A great teacher creates and inclusive atmosphere that is conducive for all learners to feel safe and encouraged to learn.
Social aspects
Physical aspects
Emotional aspects
Intellectual aspects
Online Persona
Tools
Twitter
Facebook
Linkedin
Research gate
Skills
Creativity and Innovation
Advanced ICT skills
Personal Management
Collaboration
Adaptive thinking
Time management
Organisation
Teaching dimensions
Professional conduct
Learner assessment and achievement
Content Knowledge
Pedagogical Knowledge
Creating Conducive learning space
Values
Truthfulness
Fairness
Loyalty
Transparency
Professional Background
An experienced highly motivated maths and science teacher in possession of Bsc , PGCE , BSc Honours and is currently enrolled for M.ED ICT at UJ. My research interests include the affordances of ICT in inclusive education/ special needs education. I employ learner centred approaches in order to develop learners into independent thinkers and problem solvers that will contribute meaningfully in the changing world. I would like to be known for breaking the odds in special needs education in terms of using ICT reduce barriers to learning.
Education Knowledge
For something to be regarded as knowledge:
It must be true
The perceiver must believe it to be true
The perceiver must be able to justify it to be the case
The framework for ways of knowing for teachers
• Emancipatory knowledge
Emancipatory knowledge is the knowledge that critically examines the context or environment in which the teaching and learning experience occur. It involves understanding political processes of the institution
• Aesthetic knowledge
Aesthetic knowledge involves the art of teaching and learning. It acknowledges that learning is an act and that one can know by acting and doing
• Personal knowledge
Personal knowledge is about understanding one’ self and the participation in the act. Personal knowledge is subjective, concrete, existential and is about being true to one’s values, intentions and actions. It is about engaging with students to help promote and achieve integrity
• Ethical knowledge
Ethical knowledge - Moral knowledge. It is about how teachers act and conduct themselves in the call of duty
• Empirical knowledge
Empirical knowledge is about what we can experience through our physical senses. It is about seeking conscious reasoning, problem solving, predicting, explaining and describing to develop theories
Knowledge Types
Knowledge of things- Knowledge what
E.g I know my friends, Johannesburg etc
Practical Knowledge - Knowledge how
e.g I know how to bulid a model of a crane
Factual Knowledge -Knowledge that
e.g I know 1 +1 = 2