по Jordan Magembe 2 лет назад
159
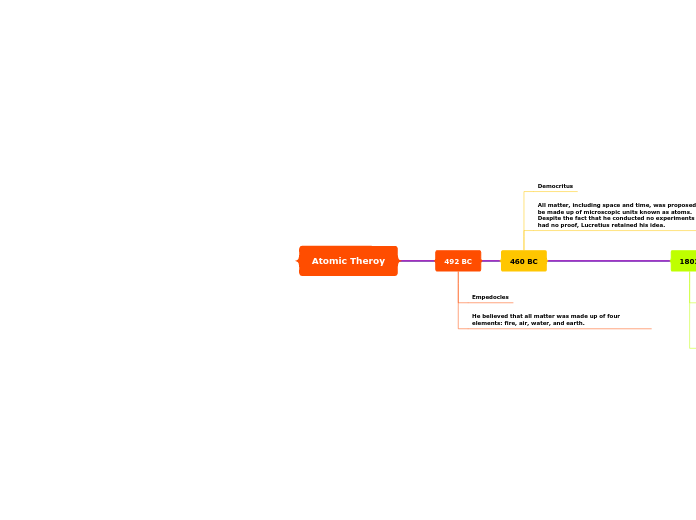
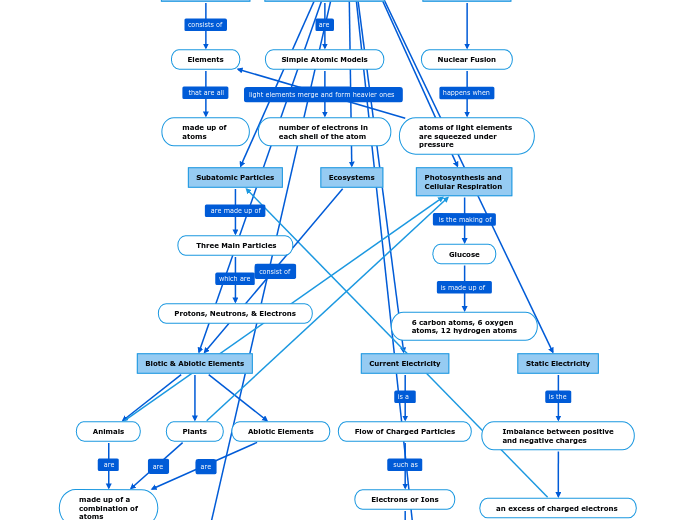
Atomic Theroy
The development of atomic theory has been marked by significant discoveries from various scientists throughout history. Henri Becquerel's discovery of radioactivity in 1896 laid the foundation for understanding atomic behavior, and in 1897, J.