Example
If we purchase a bond with a price RM1000,(P) coupon rate 10%(C) and maturity of 10 years (n=10) wee will gate YTM 10%
FORMULA CALCULATE YTM
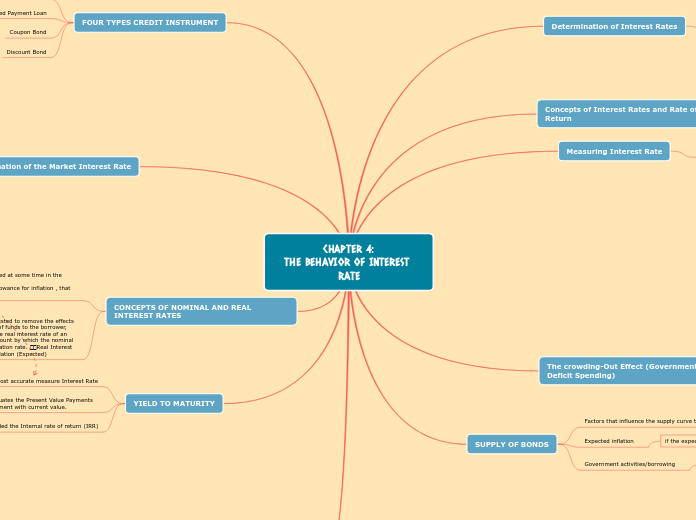
CHAPTER 4:
THE BEHAVIOR OF INTEREST RATE
This ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa is one of the most spectacular of the ancient world. Find out more about the people of Ancient Egypt, their gods and goddesses, magical land and daily life.
SUPPLY OF BONDS
Government activities/borrowing
decision by governments can affect bond prices and interest rates in the economy.
Expected inflation
if the expected inflation increased, the real interest rate falls.
Factors that influence the supply curve to shift
Expected profitability of investment opportunities
SHIFTS IN BOTH DEMAND AND SUPPLY OF BONDS
The liquidity preference framework
The keynesian approach focuses on the supply of money and demand of money.
Total wealth= total money + total Q of bonds in economic.
Keynes holding highly liquid money:
*Transaction
*Precaution
*speculation
CHANGES IN EXPECTED INFLATION : THE FISHER EFFECT
*expected inflation ↑,expected return on bond relative to real assets or goods falls for any given price and interest rate.
*When expected inflation rises, interest rates will rise.
*When expected inflation fallen, interest rates will fall.
The crowding-Out Effect (Government Deficit Spending)
supplier/ seller bond = demander loanable fund
Demander/ buyer bond =
Supplier loanable fund
YIELD TO MATURITY
Egyptian Art has a major role in conveying the essential traits of this great civilization.
The Egyptian art portrays best what this civilization valued the most, what people looked like, how they dressed, the jobs they had, etc.
YTM also called the Internal rate of return (IRR)
YTM is interest rate that equates the Present Value Payments received from a debt instrument with current value.
YTM is the most accurate measure Interest Rate
Period
Periods in Ancient Egyptian art
Type in the 6 periods in the Egyptian art. Example: Old Kingdom (2680 BC-2258 BC) .
Measuring Interest Rate
Yield to Maturity
Concepts of Interest Rates and Rate of Return
Rates of Returns (ROR)
Interest Rate
CONCEPTS OF NOMINAL AND REAL INTEREST RATES
Real Interest Rate
An interest rate that has been adjusted to remove the effects of inflation to reflect the real cost of funds to the borrower, and the real yield to the lender. The real interest rate of an investment is calculated as the amount by which the nominal interest rate is higher than the inflation rate. ��Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation (Expected)
Nominal Interest Rate
Is the rate of interest that is accrued at some time in the future
Nominal interest rate makes no allowance for inflation , that is, it ignores the effects of inflation
Determination of the Market Interest Rate
Interest Rate Determination in a Economic System
An Introduction(Demand and Supply in the Credit market)
Subtopic
Theory of Asset Demand
All the determining factors above can be assembled into the theory of asset demand
The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its liquidity relative to alternative assets
The quantity demanded of an asset is negatively related to the risk of its returns relative to alternative assets
The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its expected return relative to alternative assets
The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to wealth
Determinants of Asset Demand
An asset is a piece of property that is a store of value
1. Wealth
2. Expected return
3. Risk
4. Liquidity
Determination of Interest Rates
The classical model
FOUR TYPES CREDIT INSTRUMENT
Discount Bond
Egyptians wore make-up and jewelry because they believed this made them more attractive for the Gods. Also, jewelry was a sign of wealth - the more jewelry someone had, the richer he/she was.
Coupon Bond
Fixed Payment Loan
Simple Loan