по Fatima Nuñez 6 лет назад
2637
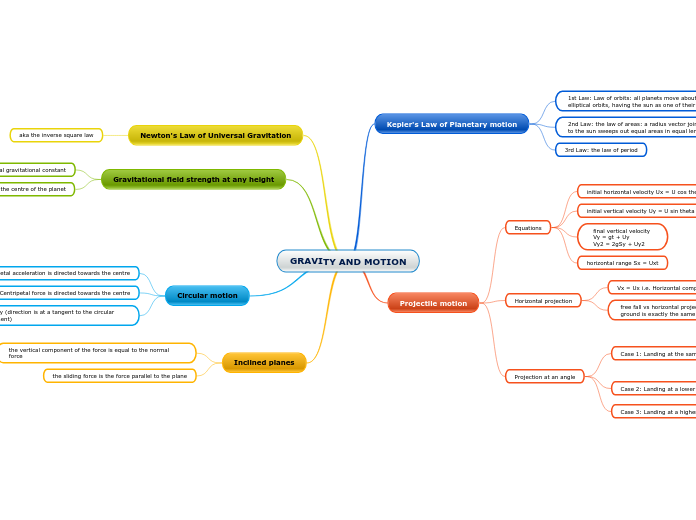
Circular Motion
Banked turns involve a vehicle inclining towards the inside of a curve, which is common on highway on-ramps to accommodate higher speeds. In circular motion, centripetal force is the unbalanced force that acts towards the center of the circle, keeping the object in uniform circular motion.