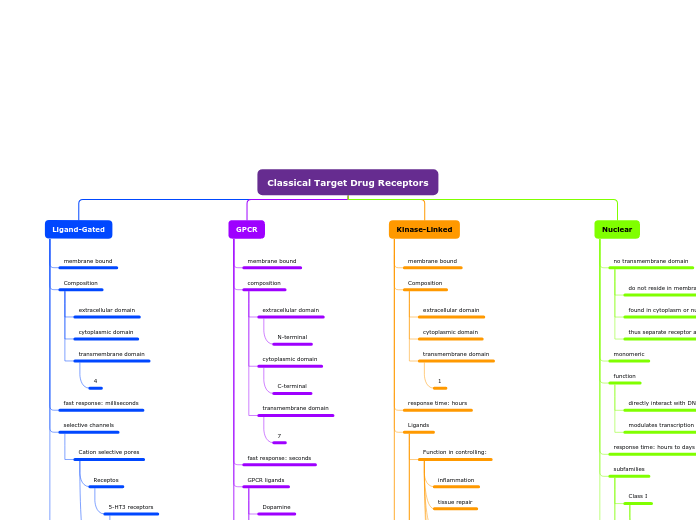
Classical Target Drug Receptors
Nuclear
Might contain or have a non-genomic target interacting directly with cytosolic proteins
subfamilies
Class III
small includes receptors for
Vit. D receptor
Thyroid hormones
form obligate heterodimers with RXR
Hybrid class
Class II
include receptors for
xenobiotic
Cyt. P3A for metabolization of drugs
cholesterol
fatty acids
form heterodimers with RXR (retinoid x receptor)
found in nucleus
Class I
primary receptors to steroid hormones
estrogen, progesterone, and androgen
mineralocorticoids
glucocorticoids
form homodimers
found in cytoplasm
response time: hours to days
function
modulates transcription
directly interact with DNA
monomeric
no transmembrane domain
thus separate receptor and DNA binding domains
found in cytoplasm or nucleus of cell
do not reside in membrane
Kinase-Linked
Kinase Receptors
Cytokine Receptors
associated with cytosolic tyrosine kinases (JAK)
no intrinsic kinase activity
Serine/Threonine Kinase
TFG receptor
RTK
TLRs
bacterial infection mediate response
growth factor receptors (EGF and NGF)
End Result: activation or inhibition of nuclear transcription factors by:
suppression or activation of target genes
Ligands
hormones
types
bacterial lipopolysaccharides
insulin
cytokines
growth factors
Function in controlling:
immune response
apoptosis
cell cycle progression
tissue repair
inflammation
response time: hours
1
GPCR
desensitization
Receptor internalization
endocytosis
downregulation of receptor
phosphorylation
Protein Kinase A and C
nonspecific kinases
threorine and serine
GPCR Subfamilies
Subtopic
metabotropic Glu Receptor/Ca Sensor
small groups
GABAb receptors
Secretin/glucagon
intermediate EC tail
peptide hormones
calcitonin
Rhodopsin
short EXC tail on N-terminal
ligands bind to helices of EXC hoops
largest group
purines
neuropeptides
amine neurotransmitters
protanoids and cannabinoids
GPCR ligands
Act on different types of receptors
5-HT
ACh
Opioids
Dopamine
fast response: seconds
composition
7
C-terminal
N-terminal
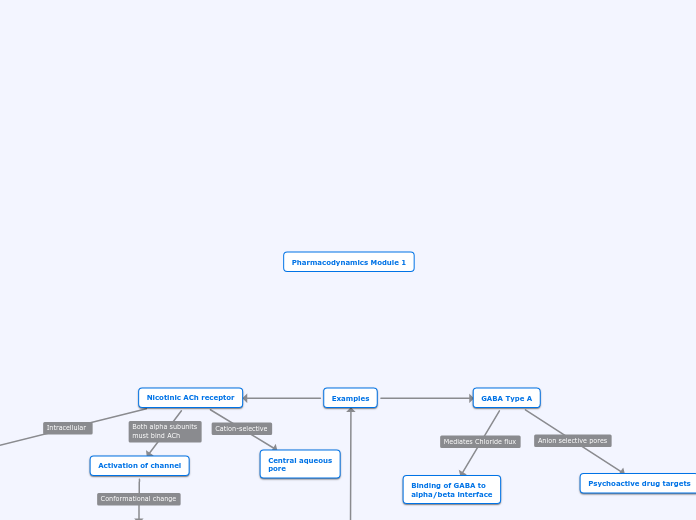
Ligand-Gated
other biological ligands
respond to intracellular binding signals
atp recepots
calcium binding receptors
arachadonic acid sensitive receptors
selective channels
Cation selective pores
anion selective pores
Receptors
GABA
mediate chloride transport
Receptos
5-HT3 receptors
drug target of psychoactive drugs
fast response: milliseconds
Composition
transmembrane domain
4
cytoplasmic domain
extracellular domain
membrane bound