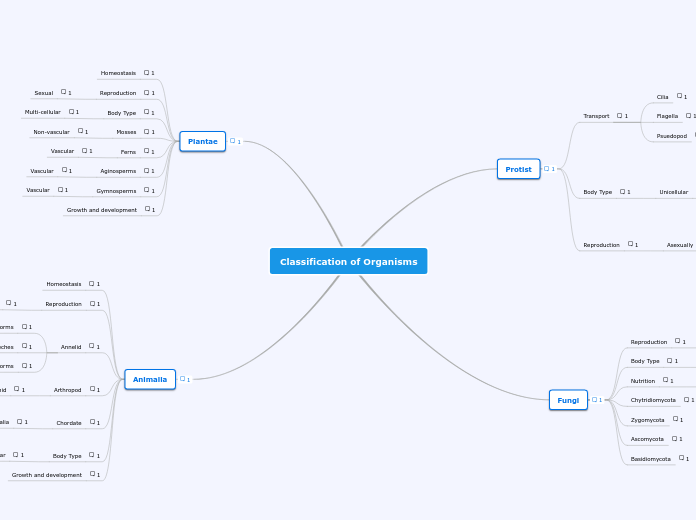
Classification of Organisms
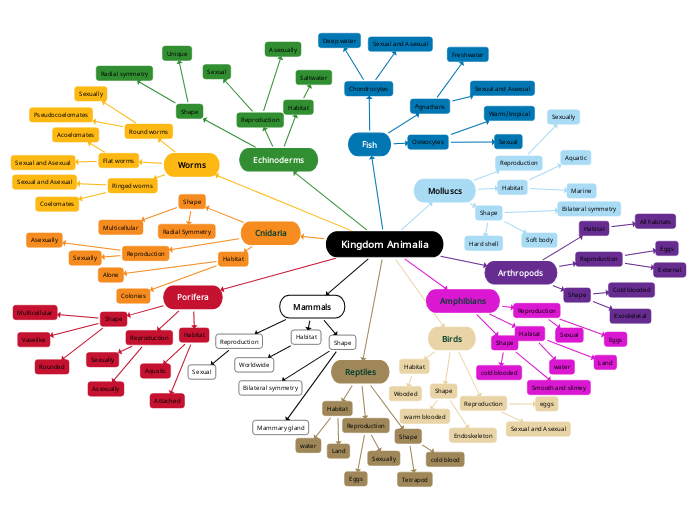
Animalia
Kingdom for all animals!
Start as an embryo and then develops into a full organism.
Chordate
Phylum for mammals.
Mammalia
Class for Mammals
Primates
Mammals with grasping fingers
Hominidae
Primates with upright posture family
Homo
Genus of primates with an s-curved spine
Homo sapien
Human species
Carnivora
Order for carnivores
Felidae
Family for cats
Panthera
Genus for roaring cat
Panthera leo
Species of Lion
Arthropod
Phylum for invertebrates with exoskeletons.
Arachnid
Class of spiders, scorpions, and others.
Scorpiones
Class of scorpion
Scorpionoidea
Family of scorpion
Pandinus
Genus of scorpion
Pandinus imperator
Species of emperor scorpion
Annelid
Phylum for segmented worms.
Segmented worms
Leeches
Earthworms
Type of annelid
Sexually
Plantae
Kingdom for all plants!!
Growth and development
start as seeds, then germinate, then grow.
Gymnosperms
Aginosperms
Ferns
Vascular
These are vascular plants
Mosses
Phylum of plantae
Non-vascular
These are non-vascular plants
Reproduction means
Sexual
Male and female organs
Homeostasis
The organs/organelles inside of the organisms help regulate the pH
Fungi
Kingdom for the FUNGI!!
Basidiomycota
Ascomycota
Zygomycota
Chytridiomycota
Phylum of Fungi
Nutrition
How Fungi get nutrition
Absorption
The transport of food from their substrate into their cell walls
Multi-cellular
Means of reproduction
Sexual and asexual
Can reproduce like plants, or can spread
Protist
Kingdom for all protists!!!
Reproduction
Multi-cellular body type
Asexually
One organism that splits
Body Type
How they are made up
Unicellular
Most are unicellular
Algea
Algea are unicellular protists
Dinoflagellates
Diatoms
Chrysophytes
Euglenophytes
Phylum of algea
Transport
Transportation
Psuedopod
'False foot'. A little extenuation to allow a protist to move.
Flagella
Whip-like tail to allows the organism to move
Cilia
Little hairs to help move