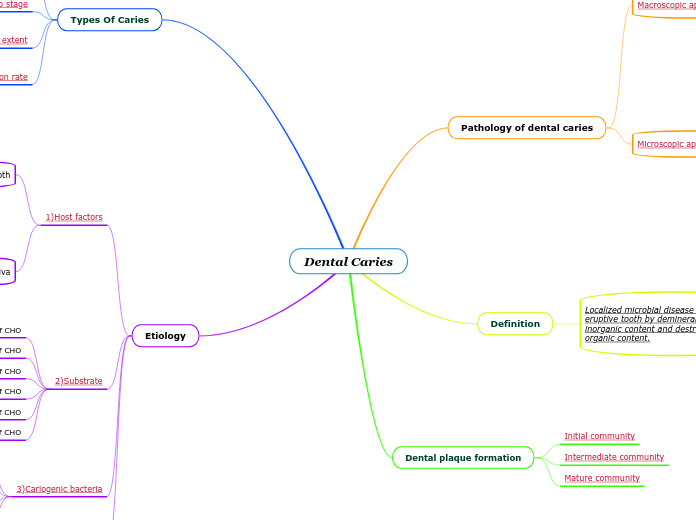
Dental Caries
Etiology
4)Time
3)Cariogenic bacteria
Adhesiveness
Form intra&extracellular polysaccharides
Acidouric
Acidogenic
2)Substrate
Refinement of CHO
Local effect of CHO
Texture of CHO
Frequency of CHO
Amount of CHO
Type of CHO
1)Host factors
saliva
Antibacterial effect
Buffering capacity
Salivary glycoproteins
Washing effect
Susceptible tooth
Genetic factors
Fluorides
Structure
Morphology
Position
Types Of Caries
According to progression rate
1; rumpant caries 2;acute caries 3; chronic caries 4;arrested caries
According to extent
1;primary caries 2; secomdary caries
According to stage
1;spot 2;enamel caries 3; dentin caries 4; deep dentin caries
According to site
1;pits and fissure caries 2;smooth surface caries 3; root caries
Dental plaque formation
Mature community
Intermediate community
Initial community
Definition
Localized microbial disease affecting post eruptive tooth by demineralizing its inorganic content and destruction of its organic content.
Pathology of dental caries
Microscopic appearance
Histopathology of DENTIN caries
Superficial zone
Infected lesion
Liquefaction foci and transverse clefts
Beading
Bioneers
Uninfected lesion
Zone of hypomineralization
Zone of hypermineralization
Zone of fatty degeneration
Histopathology of ENAMEL caries
Phase of secondary enamel caries
Phase of destruction
Phase of bacterial invasion
Phase of initiation
Macroscopic appearance
White chalky spot Then becomes Brown spot