по Rachel Stewart 5 лет назад
136
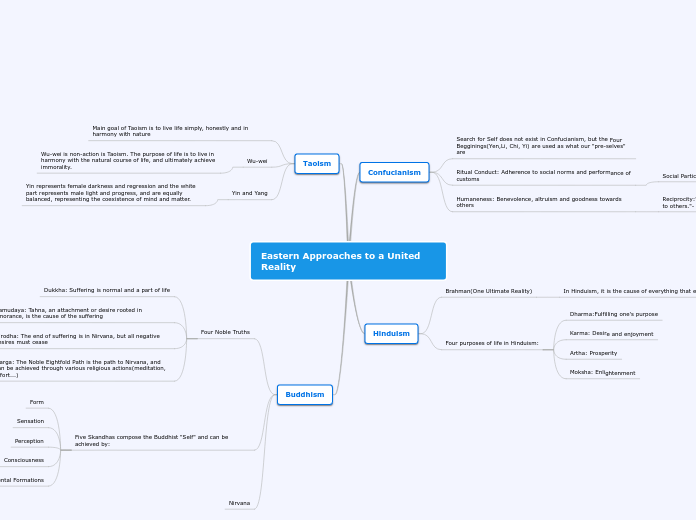
Eastern Approaches to a United Reality
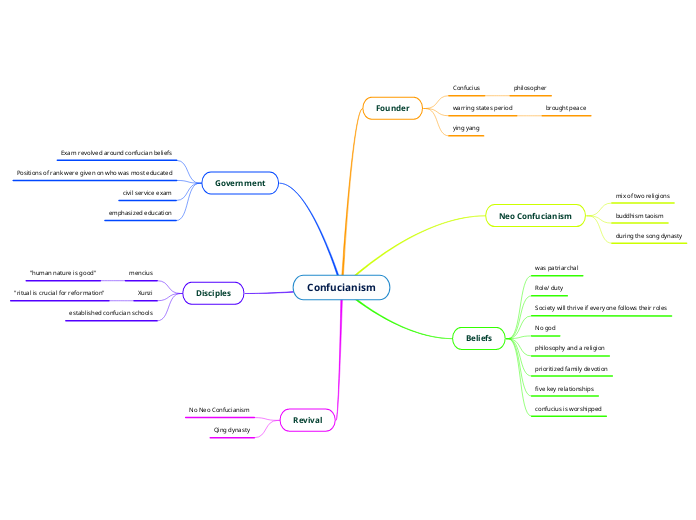
The Eastern philosophical traditions of Taoism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Confucianism each offer unique perspectives on living a harmonious life and understanding reality. Taoism emphasizes simplicity, honesty, and living in harmony with nature through principles such as Yin-Yang and the concept of Wu-wei, which advocates for non-action and alignment with life'