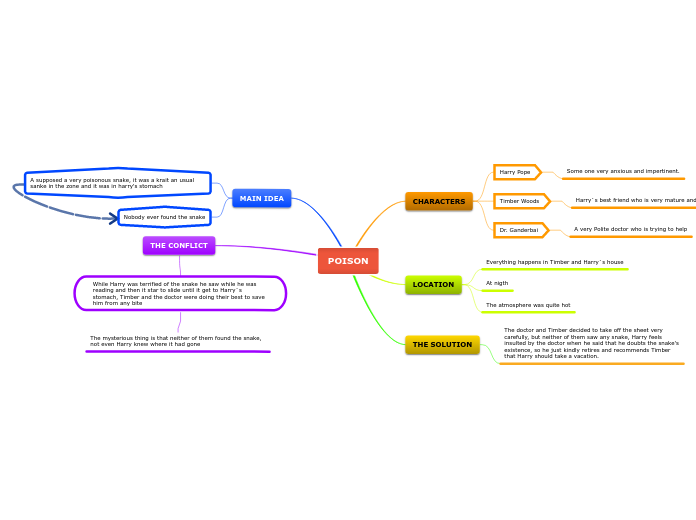
по Teegan Moore 3 лет назад
214
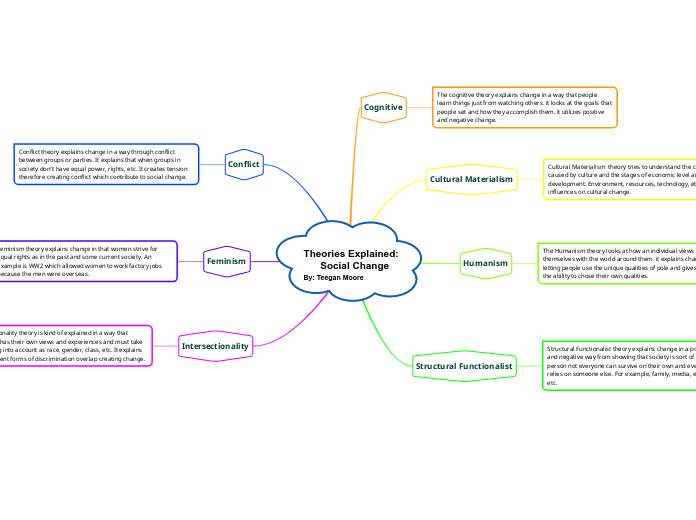
Theories Explained: Social Change By: Teegan Moore
Various theories attempt to explain social change through different perspectives. Cultural Materialism attributes change to factors such as environment, resources, and technology, emphasizing the economic and natural stages of development.