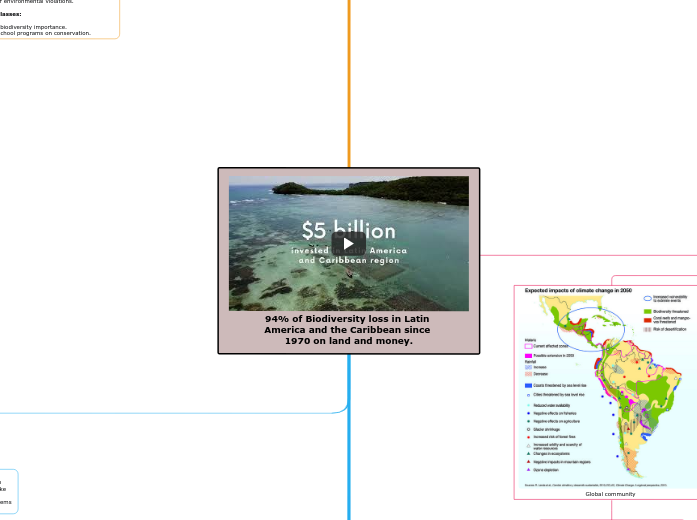
94% of Biodiversity loss in Latin America and the Caribbean since 1970 on land and money.
Add the name of the author.
Why?
Subtopic
Loss of biodiversity is being driven by human activities, which include deforestation for agriculture and urbanization, climate change, and weak environmental law enforcement. Loss of biodiversity threatens all three pillars of sustainability: socially, public health threats and economic hardships among indigenous and others dependent on biodiversity livelihoods. Some of the economically poor businesses that will be affected include agriculture, fishing, and ecotourism, while tree loss causes climatic change. Loss of an ecosystem weakens the global environment through reduction of the essential services of soil maintenance, water filtering, and storage of carbon.
Where?
This issue effects Central America, parts of the Caribbean and Latin America. With the Amazon Rainforest in countries like Brazil, Peru and Colombia are main areas of concern. Also other ecosystems like tropical forests, wetlands and coastal areas.
What?
With a 94% decrease since 1970, biodiversity loss in Latin American and the Caribbean refers to the dramatic drop in species diversity and ecological health. Human activities like illegal logging, deforestation, and agriculture are the main causes of this loss. This quick reduction has made ecosystems weaker, such as rainforests. wetlands, and coral reefs.
Solution Locally and Nationally
Nationally
Stronger Environmental Laws:
- Enforce regulations against deforestation and illegal activities.
- Impose penalties for environmental violations.
Public Awareness classes:
- Educate citizens on biodiversity importance.
- Launch media and school programs on conservation.
Locally
Empower Indigenous Communities:
- Recognize Land rights
- Support sustainable land management and conservation.
-Involve in decision-making.
Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry:
- Promote agroforestry and sustainable farming.
- Provide training and certification for sustainable products.
When?
This biodiversity loss has been increasing every year since 1970, With a massive increase theses past decades, mainly from 1990 due to increase of deforestation and industrial expansion. Human activity's also worsens the situation like littering.
Who?
You can add here people, places or events that took part in the author's character formation.
Indigenous communities and Environmental Organization
The indigenous will always advocate for the protection of biodiversity due to the fact of cultural survival, environmental health and sustainability.
Governments
governments frequently put economic growth (such as mining and agriculture) ahead of conservation, which may delay attempts to protect the environment.
Global community
The global community is very concerned with the
biodiversity loss and connection on climate change
and the well being of people/society.
Connections to a Geographic Perspective
Social, Environmental and Economic
Economic
The financial loss of biodiversity undermines the industries dependent on healthy ecosystems-namely agriculture, fisheries, and ecotourism. Such degradation results in reduced yields by agriculturalists; fisheries deplete their resources as natural attractions used in tourism erode. When contaminated, jobs disappear and livelihoods are compromised at the increasing cost of poverty. In a lot of cases, national governments seem to favor immediate economic gains from other sectors like mining and urbanization at the cost of the long-term sustainability of biodiversity.
Environmental
Loss of biodiversity, from an environmental perspective, has a direct impact on important ecosystem services like soil fertility, water purification, and carbon sequestration. These services are essential for ecological balance and controlling climate change. The loss of species and habitats compromises the resilience of ecosystems in times of crisis, and increases soil erosion, water droughts, and the intensity of extreme weather events.
Social
The social consequences of biodiversity losses in Latin America and the Caribbean. Ecosystem erosion threatens ways of life and livelihoods, particularly those of indigenous peoples, whose cultural practices are closely tied to the environment. Most groups depend on biodiversity for food and subsistence, and ecosystem degradation can threaten displacement and loss of cultural continuity.