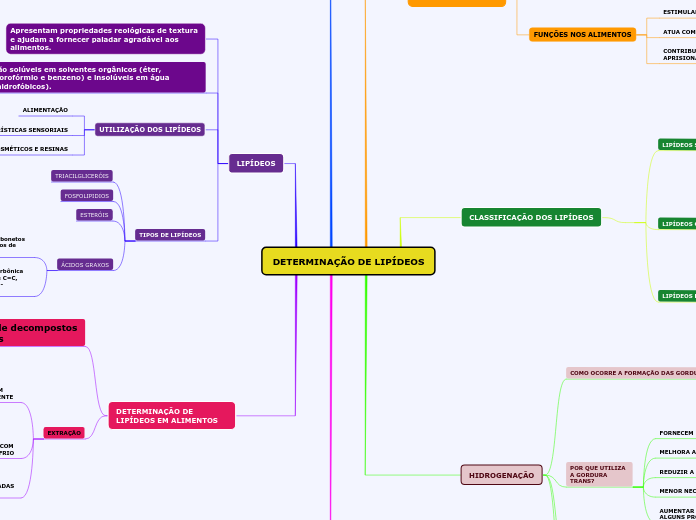
DETERMINAÇÃO DE LIPÍDEOS
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
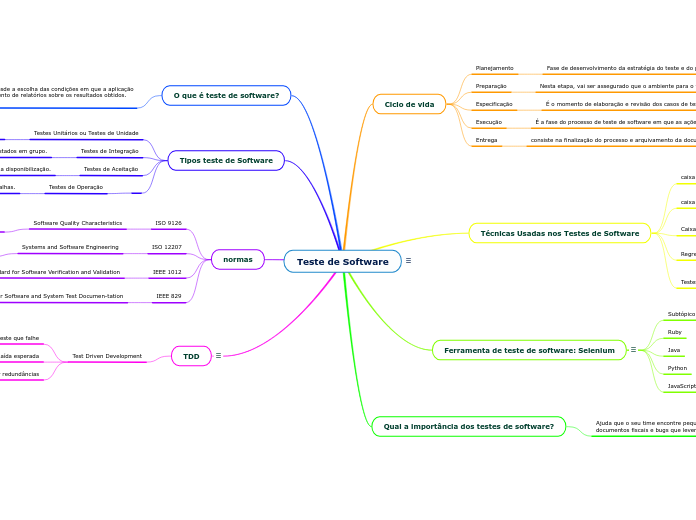
DEGRADAÇÃO DE LIPÍDEOS
ABSORÇÃO DE SABORES/ODORES ESTRANHOS
PIRÓLISE
HIDRÓLISE
OXIDAÇÃO
DEPRECIAÇÃO DO PRODUTO E TOXIXIDADE
VALOR NUTRICIONAL
QUALIDADE SENSORIAL
DETERMINAÇÃO DE LIPÍDEOS EM ALIMENTOS
EXTRAÇÃO
EXTRAÇÃO DE GORDURAS LIGADAS A OUTROS COMPONENTES
HIDRÓLISE ALCALINA
HIDRÓLISE ÁCIDA
EXTRAÇÃO COM SOLVENTE FRIO
MISTURA DE TRÊS SOLVENTES CLOROFÓRMIO - METANOL - ÁGUA
EXTRAÇÃO COM SOLVENTE QUENTE
PESAGEM DE GORFURA EXTRAÍDA
EVAPORAÇÃO DO SOLVENTE
EXTRAÇÃO DE GORDURA COM AMOSTRA DE SOLVENTE
Baseada na diferença de solubilidade decompostos solúveis em determinados solventes
LIPÍDEOS
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
TIPOS DE LIPÍDEOS
ÁCIDOS GRAXOS
Ácido graxo insaturado - A cadeia carbônica contêm uma ou mais ligações duplas C=C, podendo ser monoinsaturada ou poli-insaturada
Ácido graxo saturado - Cadeia de hidrocarbonetos só contêm ligações simples entre os átomos de carbono.
ESTERÓIS
FOSFOLIPIDIOS
TRIACILGLICERÓIS
UTILIZAÇÃO DOS LIPÍDEOS
Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above.
SABÕES, COSMÉTICOS E RESINAS
CARACTERÍSTICAS SENSORIAIS
ALIMENTAÇÃO
São solúveis em solventes orgânicos (éter, clorofórmio e benzeno) e insolúveis em água (hidrofóbicos).
Apresentam propriedades reológicas de textura e ajudam a fornecer paladar agradável aos alimentos.
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
CARACTERIZAÇÃO DE ÓLEOS E GORDURAS
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
ÍNDICE DE TBA
ÍNDICE DE PERÓXIDO
Attributive clauses serve as an attribute to a noun (pronoun) in the main clause. This noun or pronoun is called the antecedent of the clause.
ÍNDICE DE ACIDEZ
An adverbial clause is a group of two or more words that function as an adverb in a sentence.
RANCIDEZ HIDROLÍTICA
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
RANCIDEZ OXIDATIVA
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
ÍNDICE DE SAPONIFICAÇÃO
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
HIDROGENAÇÃO
É a adição de hidrogênio nas insaturações dos ácidos graxos insaturados, permitindo transformar óleos em gorduras semi-sólidas.
EFEITOS DAS TRANS NA SAÚDE
Diminui HDL-C “bom colesterol”
Aumenta LDL-C “mau colesterol”
POR QUE UTILIZA A GORDURA TRANS?
AUMENTAR A VIDA DE PRATELEIRA DE ALGUNS PRODUTOS
MENOR NECESSIDADE DE REFRIGERAÇÃO
REDUZIR A PROBABILIDADE DE FICAR RANÇOSO
MELHORA A CONSISTÊNCIA
FORNECEM MELHOR SABOR
COMO OCORRE A FORMAÇÃO DAS GORDURASTRANS?
Biohidrogenação
Elaboração de frituras (200oC)
Hidrogenação Industrial
Operações de extração, refino e armazenamentode óleos vegetais
CLASSIFICAÇÃO DOS LIPÍDEOS
IMPORTÂNCIA DOS LIPÍDEOS NA DIETA
FUNÇÕES NOS ALIMENTOS
An adverbial is an individual word (that is, an adverb), a phrase, or a clause that can modify a verb, an adjective, or a complete sentence.
CONTRIBUI NA AÇÃO DE LEVEZA E APRISIONAMENTO DE MASSAS E SORVETES
ATUA COMO TRANSPORTE DE CALOR, NAS FRITURAS
ESTIMULAM PRAZER COM A COMIDA
FUNÇÕES NO CORPO
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
TRANSPORTADOR DE VITAMINAS LIPOSSOLÚVEIS
IMPORTANTE FONTE CALÓRICA NA DIETA
FORNECEM ISOLAMENTO QUE RETÉM O CALOR DO CORPO
The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed.
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.
AJUDA A PROTEGER ÓRGÃOS INTERNOS
The direct object is the receiver of the action mentioned in the sentence.