av Diana chantre för 1 år sedan
89
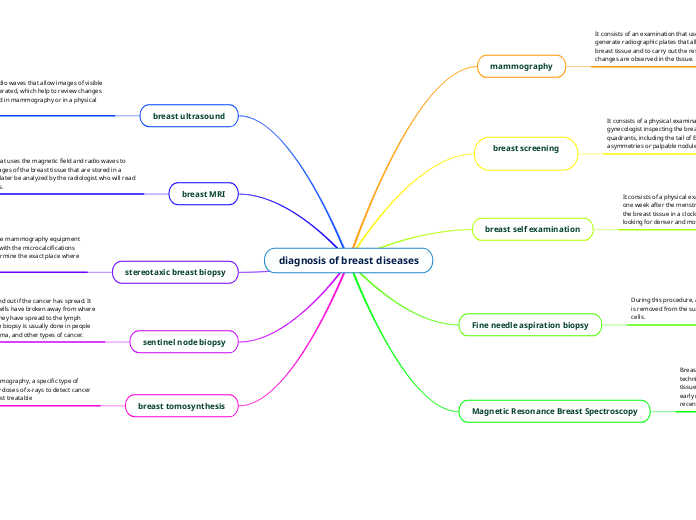
diagnosis of breast diseases
Mammography is a diagnostic tool utilizing ionizing radiation to create radiographic images of breast tissue, recommended annually for women aged 40 to 54 and biennially for those over 55.