av Mauricio Mossi för 3 årar sedan
176
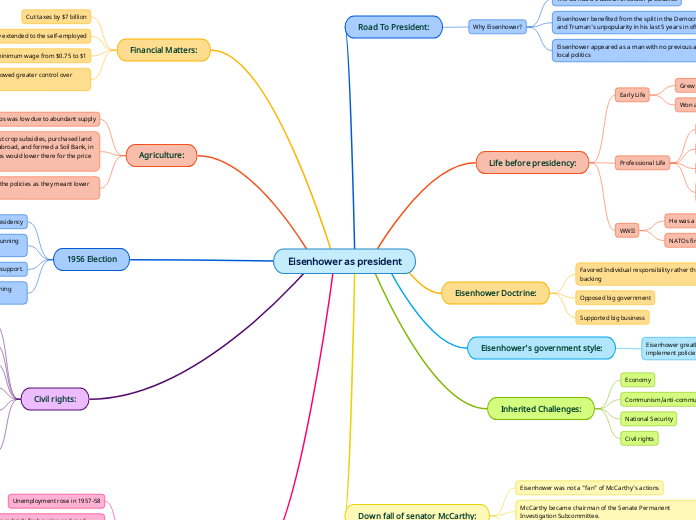
Eisenhower as president
Eisenhower, known for his leadership during WWII and as NATO's first supreme commander, grew up in Kansas and attended West Point. As president, he opposed big government, favored big business, and supported individual responsibility.