av XOsamirahXO M för 4 årar sedan
292
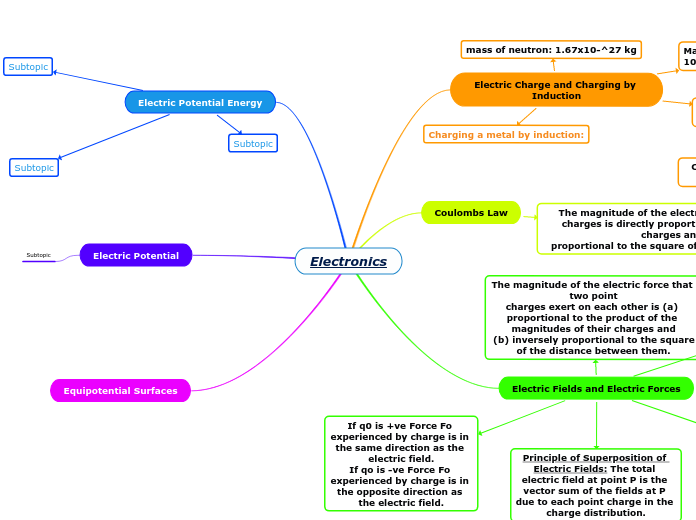
Electronics
The behavior of electric fields and forces is governed by several fundamental principles. An electric field points towards negative charges and away from positive charges. The direction of the force experienced by a charge depends on the sign of the charge relative to the field.