av stephen rofe för 6 årar sedan
218
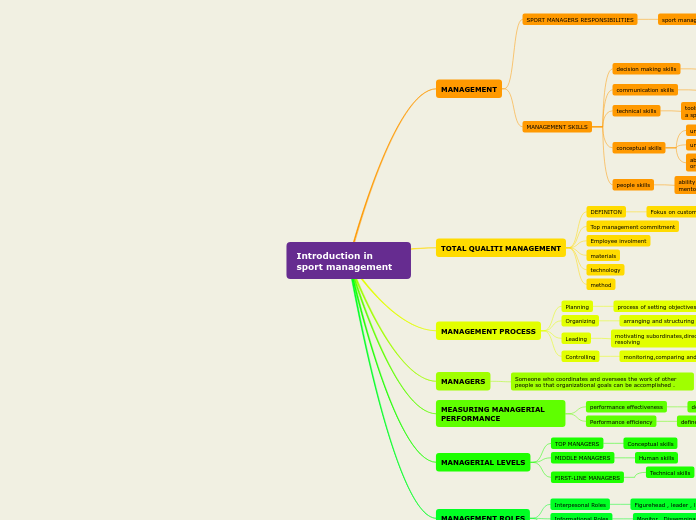
Exam Revision
The human body has various systems and structures that play essential roles in physical performance and movement. Joints are crucial for enabling movement, with different types such as hinge and ball-and-socket joints allowing various ranges of motion.