Full clause
A non-finite or verbless clause can be expanded into a full clause with a finite verb
example
While running for the bus, I slipped on the ice and fell.
While I was running for the bus, I slipped on the ice and fell.
Grammar IV
FINITE
AND
NON-FINITE
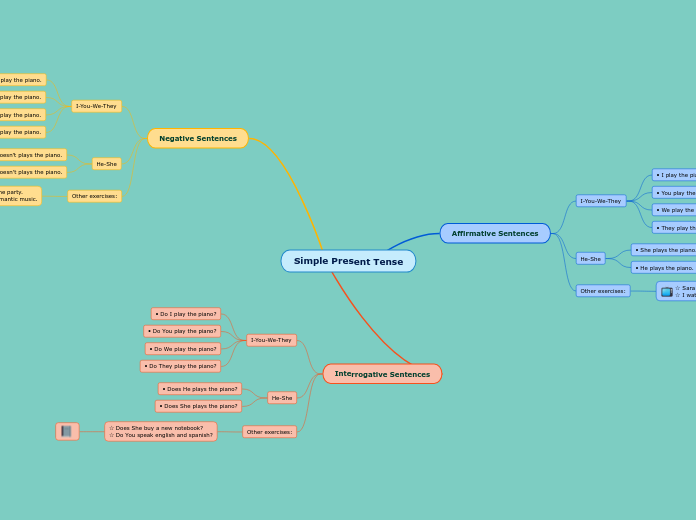
Non-finite and Verbeless clauses
Non-finite and verbless clauses have generally been treated as phrases in traditional grammar
VERBELESS CLAUSES
A verbless clause is a subordinate clause that has no verb in it at all.
Example:
- Though still in our shirt sleeves, we set to work.
NON-FINITE CLAUSES
A non-finite clause is a subordinate clause that has only a non-finite verb, in it.
Verbal noun
Example:
- By sailing round the world on her own, she showed incredible courage.
Participle
Example:
- Sailing round the world, Nancy visited many fascinating and exotic places.
Infinitive without -to
Example:
- All I did was break her window.
Infinitive with -to
Example:
- I only wanted to help you.
Verbal Noun
Example:
- Singing is easy.
Finite and non-finite verbs
NON-FINITE VERBS
Does not indicate tense
Gerund
Example:
- Being very proud of her new car, she washes it every single day.
Past Participle
Example:
- Worried by the cost of petrol, she has bought a smaller car.
Infinitive
Example:
- To buy a new car, Olga needs a bank loan.
FINITE VERBS
Indicate tense
Example:
- Olga has a new car.
- Olga and John go everywhere in their new car.
COLLOCATIONS
A collocation is a combination of two or more words which frequently occur together.
VERB+ADVERBS
Example
- She placed her keys gently on the table and sat down.
- Mary whispered softly in John's ear.
- I vaguely remember that it was growing dark when we left.
"The boy whispered softly to his mother"
VERB+PREPOSITIONS
Example
- We had to return home because we had run out of money.
- At first her eyes filled with horror, and then she burst into tears.
- Their behaviour was enough to drive anybody to crime.
"The little girl burst into tears"
ADVERB+ADJECTIVE
Examples
- Invading that country was an utterly stupid thing to do.
- We entered a richly decorated room.
- Are you fully aware of the implications of your action?
"They are happily married"
ADJECTIVE+NOUN
Examples
- The doctor ordered him to take regular exercise.
- The Titanic sank on its maiden voyage.
- He was writhing on the ground in excruciating pain.
"The second edition it's going to be published next year"
NOUN+NOUN
Example
- Let's give Mr Jones a round of applause.
- The ceasefire agreement came into effect at 11am.
- I'd like to buy two bars of soap please.
"By a struck of luck I found my keys in the rubbish bin!"
NOUN+VERB
Example
- The lion started to roar when it heard the dog barking.
- Snow was falling as our plane took off.
- The bomb went off when he started the car engine.
"The economy boomed in the 1990s"
VERB+NOUN
Example
- The prisoner was hanged for committing murder.
- I always try to do my homework in the morning, after making my bed.
- He has been asked to give a presentation about his work.
"I was also impressed by the working conditions"
UNREAL PAST
INDICATIVE
Suppose/ Imagine
Understood conditions
- The conditional part of these sentences is often understood but not stated.
- As with conditional sentences, if the event referred to is real possibility, rather than imaginary, a present verb form is possible.
2. "Suppose it starts raining, what'll we do?"
1. "Imagine we won the pools!"
"Suppose someone told you that I was spy!"
"Imagine we'd never met!" (we have met)
As if / As though
- The verb forme here depends on whether the situation is true or unreal.
- Note however, that the more colloquial like does not require this verb form change. Compare
Real and Unreal
2. "You look like you've just seen a ghost." (Informal)
"You look as if you'd just seen a ghost."(Formal)
1. "You look as if you're having secomd thoughts." (true)
"He acts as if he were in charge." (Unreal, he isn't in charge)
"I feel as if an express train had hit me." (It didn´t hit me)
I'd rather/ I prefer
- I'd rather is followed by past verb forms in the same way as wishes about the present. It expresses preferences about actions.
- Both I'd rather and I'd sooner are used with normal verb forms when comparing nouns or phrases.
- I'd prefer can be used in the same way, but note that prefer in this type of sentence has an object it
- However, I'd prefer is not followed by an unreal verb form in other situations.
4. "I'd prefer tea to coffee"
"I'd prefer you to go swimming (rather than go jogging)."
3. "I'd prefer it if you didn't go"
2. "I'd rather be a sailor than a soldier" (present)
"I'd raher have lived in Ancient Greece than Ancient Rome" (past)
1. "I'd rather you didn't smoke in here"
Wishes
Hope
Wishes about simple future events are expressed with hope.
"I hope it doesn't (won't) rain tomorrow"
"I hope you('ll) have a lovely time in Portugal (on your holiday next week)"
Past time
As with present wishes the verb form after wish is one stage further back in the past. These are wishes referring to a past event, which cannot be changed.
This use of wish is common after if only to express regrets.
"I wish I hadn't eaten so much"
Would
- Would is used when the speaker wants somebody or something else to change.
- The use with would is often use to describe an annoying habit.
2. "I wish you wouldn't make such a mess."
1. "I wish he would change his mind and marry Jane."
Present/Future time
Notice the past verb form after wish.
These are wishes where you want to change a present/future state.
"I wish I had a motorbike" (I don't have one now.)
"I wish you weren't leaving (You are leaving.)
"I wish I was going on holiday with you next week" (I'm not going.)
It's time
It's time/ It's high time
These are followed by past simple or continuous, though the time referred to is unreal.
"It's time we left. It's high time I was going".
SUBJUNCTIVE
The subjunctive mood expresses wishes, conditions contrary to fact, and requests and commands.
Past Subjunctive
The Past Subjunctive is hypothetical in meaning. It is used in conditional and concessive clauses and in subordinate clauses after wish and suppose.
- If I were a rich man, I would...
- I wish the journey were over.
- Just suppose everybody were to act like you.
Present Subjunctive
The Formulaic
Subjunctive
The formulaic subjunctive is used in certain set expressions
- God save the Queen
- Long live the king
- Come what may,...
- Heaven forbid that...
- Be that as it may,...
- Suffice it to say that,...
The Mandative
Subjunctive
The Mandative Subjunctive is used in a that-clause after an expression of such notions as demand, recommendation, proposal, intention (e.g: We insist, prefer, request; It is necessary, desirable, imperative; The decision, requirement, resolution).
This use is more characteristic of AmE that BrE, but seems to be increasing in BrE.
Subtema
EXAMPLE
The employees demanded that he resign (AmE-subjunctive)
The employees demanded that he should resign (BrE-putative should)
The employees demanded that he resigns (BrE-indicative)