av MARLLEY DANIELA PAREDES MORILLO för 4 årar sedan
273
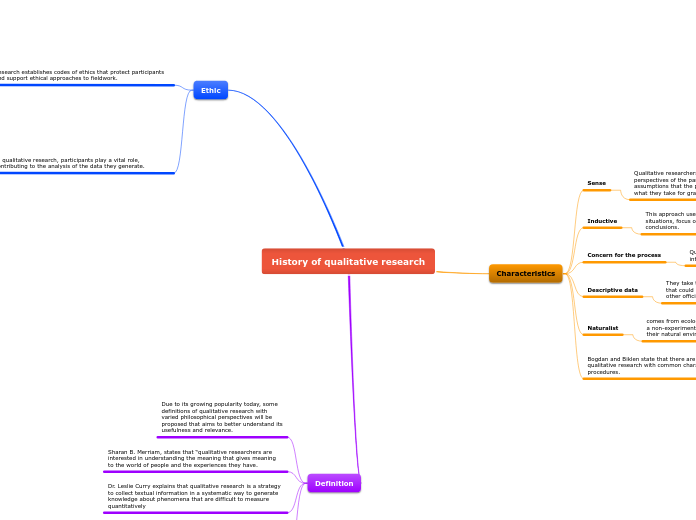
History of qualitative research
Qualitative research is distinguished by its emphasis on descriptive data in the form of words or images, such as interview transcripts, photographs, and official records. This approach employs a bottom-up, inductive method to understand situations, focusing on behaviors, building theories, and drawing conclusions.