av V. Riolo för 3 årar sedan
231
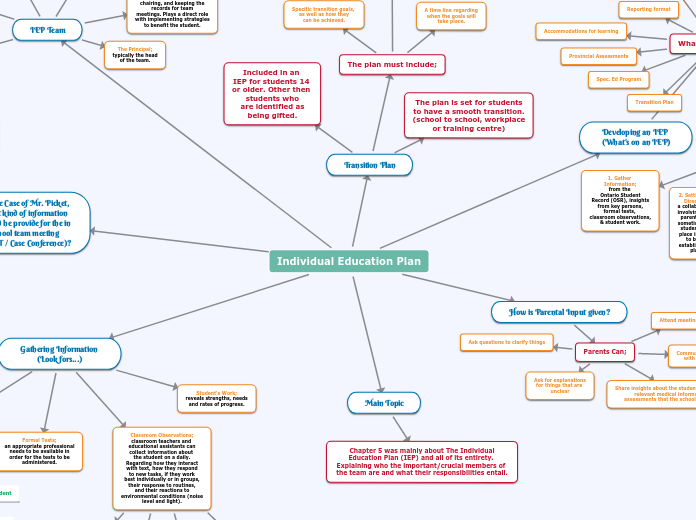
Individual Education Plan
Parental involvement in the development of an Individual Education Plan (IEP) is crucial. They can participate in meetings, share insights about their child's preferences, medical history, and assessments.