av ANGEL ER N/A för 9 årar sedan
1101
lactose mindmap_Angel Er
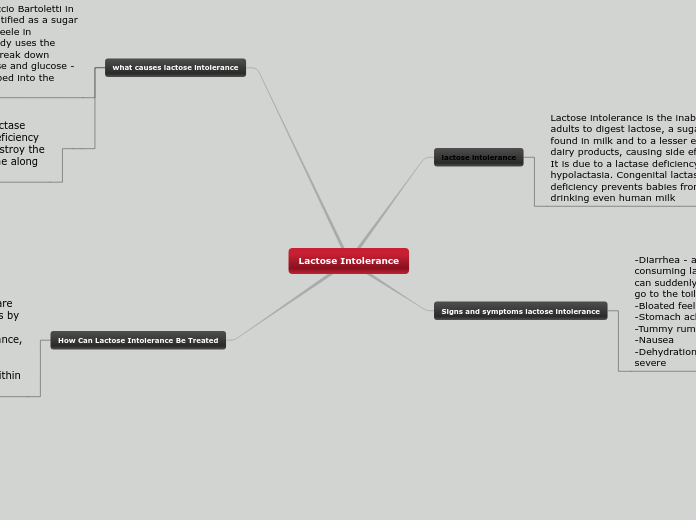
Lactose intolerance is a condition where adults cannot properly digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products, due to a deficiency in the enzyme lactase. Symptoms typically include diarrhea, bloating, stomach ache, nausea, and dehydration, which can occur shortly after consuming lactose.